Abstract
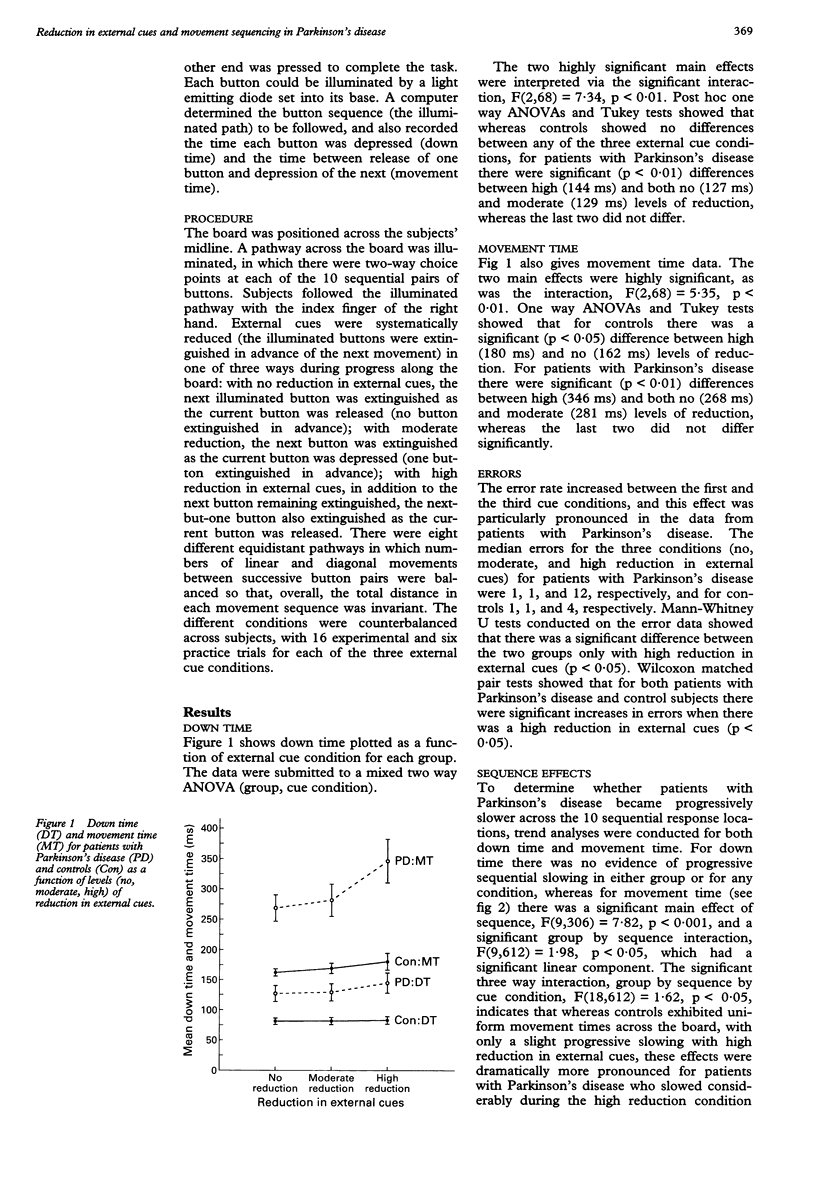
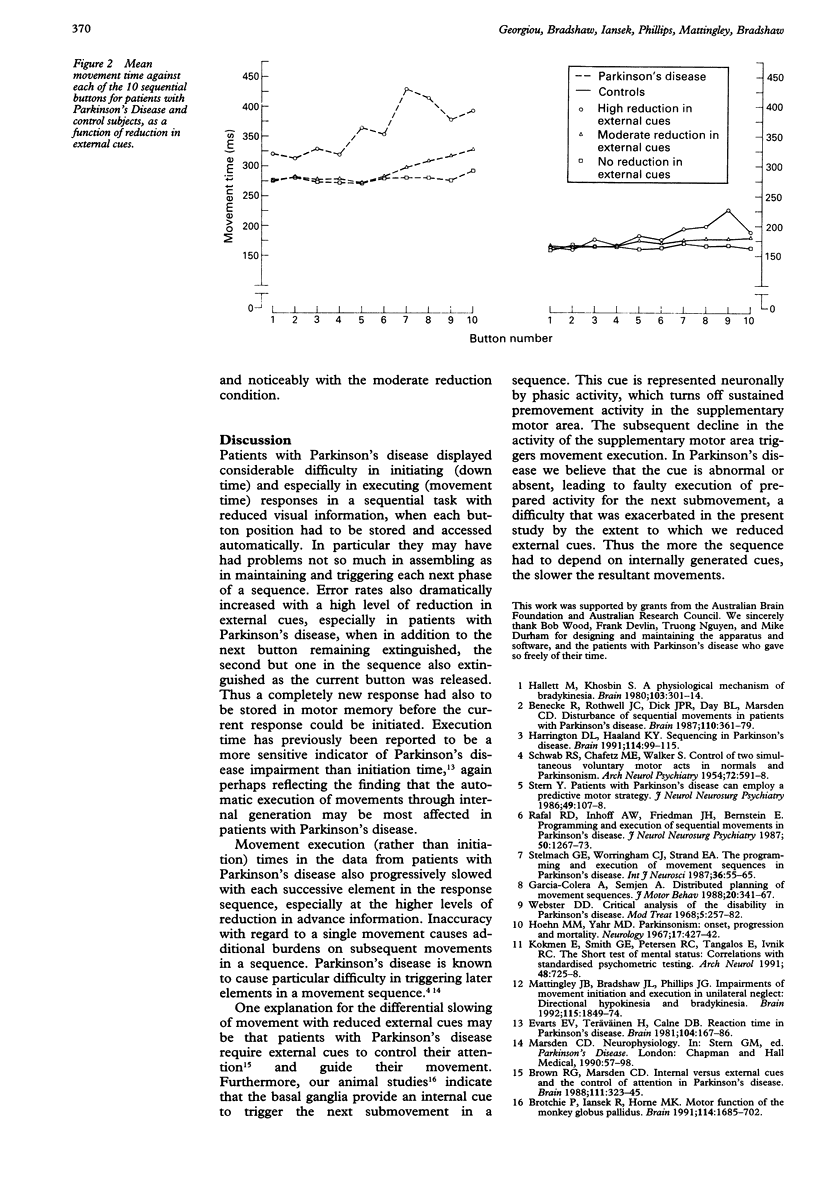
To identify the focus of impairment in the performance of sequential movements of patients with Parkinson's disease, the extent of their reliance on external cues was examined. Eighteen patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease and their matched controls performed a series of button presses at sequential choice points along a response board. The illuminated pathway to be followed successively extinguished ahead of each move according to three levels of reduction of external cues. Patients with Parkinson's disease were particularly disadvantaged with high levels of reduction of external cueing in terms both of movement preparation time (button down time) and movement execution time (movement time between buttons). Moreover, with high levels of reduction of external cueing, patients with Parkinson's disease were particularly subject to progressive slowing (movement time, not down time) further down the sequence. The basal ganglia may help generate internal cues for releasing successive stages of a predefined movement sequence.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benecke R., Rothwell J. C., Dick J. P., Day B. L., Marsden C. D. Disturbance of sequential movements in patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):361–379. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotchie P., Iansek R., Horne M. K. Motor function of the monkey globus pallidus. 2. Cognitive aspects of movement and phasic neuronal activity. Brain. 1991 Aug;114(Pt 4):1685–1702. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.4.1685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. G., Marsden C. D. Internal versus external cues and the control of attention in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1988 Apr;111(Pt 2):323–345. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V., Teräväinen H., Calne D. B. Reaction time in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1981 Mar;104(Pt 1):167–186. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Colera A., Semjen A. Distributed planning of movement sequences. J Mot Behav. 1988 Sep;20(3):341–367. doi: 10.1080/00222895.1988.10735449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M., Khoshbin S. A physiological mechanism of bradykinesia. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):301–314. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington D. L., Haaland K. Y. Sequencing in Parkinson's disease. Abnormalities in programming and controlling movement. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1A):99–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn M. M., Yahr M. D. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967 May;17(5):427–442. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokmen E., Smith G. E., Petersen R. C., Tangalos E., Ivnik R. C. The short test of mental status. Correlations with standardized psychometric testing. Arch Neurol. 1991 Jul;48(7):725–728. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530190071018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingley J. B., Bradshaw J. L., Phillips J. G. Impairments of movement initiation and execution in unilateral neglect. Directional hypokinesia and bradykinesia. Brain. 1992 Dec;115(Pt 6):1849–1874. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.6.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafal R. D., Inhoff A. W., Friedman J. H., Bernstein E. Programming and execution of sequential movements in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Oct;50(10):1267–1273. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.10.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB R. S., CHAFETZ M. E., WALKER S. Control of two simultaneous voluntary motor acts in normals and in parkinsonism. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Nov;72(5):591–598. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02330050061010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelmach G. E., Worringham C. J., Strand E. A. The programming and execution of movement sequences in Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;36(1-2):55–65. doi: 10.3109/00207458709002139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern Y. Patients with Parkinson's disease can employ a predictive motor strategy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Jan;49(1):107–108. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.1.107-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster D. D. Critical analysis of the disability in Parkinson's disease. Mod Treat. 1968 Mar;5(2):257–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


