Abstract
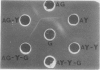
Two major antigenic components, I and II, were detected by double immunodiffusion in sonic extracts of the germinating (G) or yeast (Y) cells of the dimorphis organism, Candida albicans group A. Component I may be a heterogeneous mixture of antigens which are stable to heating and phenol. Component II is more homogeneous but is labile to heat and phenol. Rabbit antisera, showing only precipitin to component II or certain human sera at high dilution, were found to react with G cells to give an immunofluorescence which was confined to the germ tubes. This suggested that component II is localised on the germ tubes, whereas no immunofluorescent reaction against the yeast cells could be detected under the same conditions although component II was as readily extracted from these cells as from G cells. This suggested that component II might exist in a cryptic state in the Y cells. In support of the latter contention it was shown that live Y cells did not absorb precipitin to component II nor were they capable of providing these antibodies in rabbits. Using both human and rabbit sera, it was shown that the antigenic specificity of the immunofluorescence assay where Y cells were used was related to component I and that where G cells were used it was related to both components I and II.
Full text
PDF


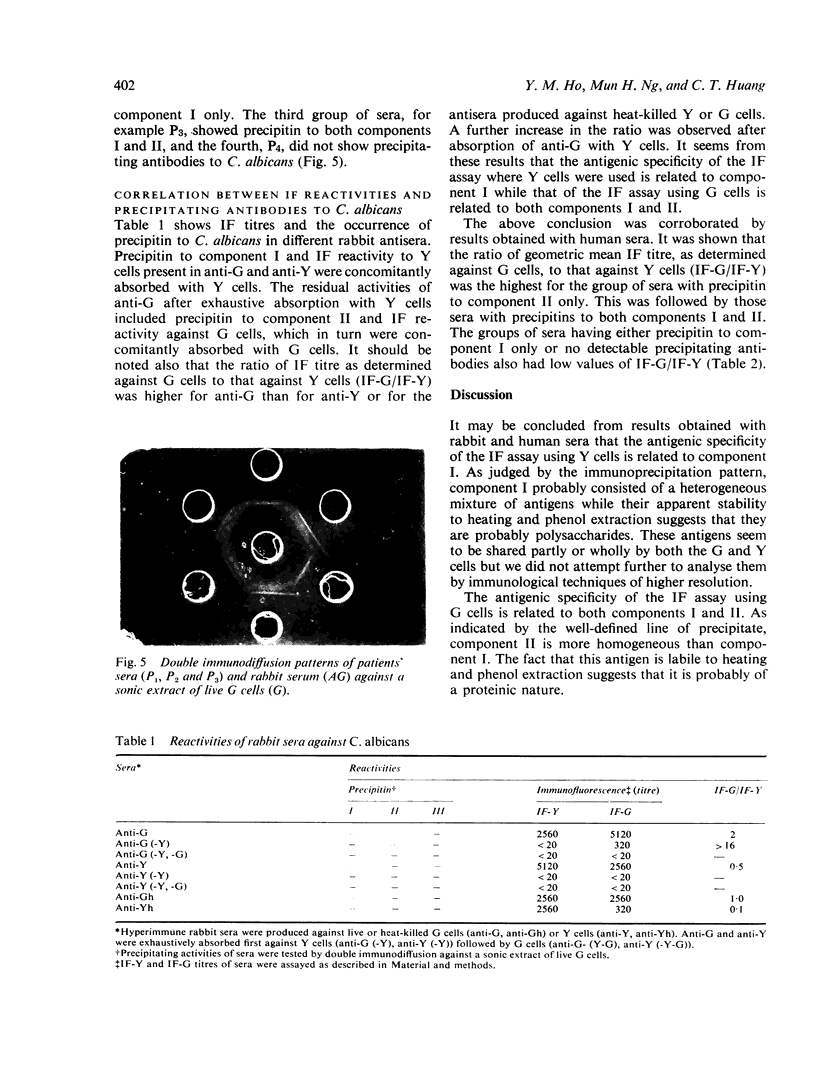



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcraft K. W., Leape L. L. Candida sepsis complicating parenteral feeding. JAMA. 1970 Apr 20;212(3):454–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Fungal infections complicating acute leukemia. J Chronic Dis. 1966 Jun;19(6):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattaway F. W., Holmes M. R., Barlow A. J. Cell wall composition of the mycelial and blastospore forms of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 May;51(3):367–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. G., Odds F. C., Richardson M. D., Holland K. T. Optimum conditions for initiation of filamentation in Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):338–342. doi: 10.1139/m75-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. G., Richardson M. D., Odds F. C., Holland K. T. Relevance of antigenicity of Candida albicans growth phases to diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 13;4(5884):86–87. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5884.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong J. S., Drummond K. N. Method for preparation of glomeruli for metabolic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):1034–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gang N. F. A rapid method for the isolation of glomeruli from the human kidney. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):267–269. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Russell E., Jr, Remington J. S. The compromised host and infection. II. Deep fungal infection. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):169–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. M., Huang C. T., Ng M. H. The occurrence of Candida in hospital patients and normal subjects. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1977 Dec;8(4):525–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. M., Ng M. H., Teoh-Chan C. H., Yue P. C., Huang C. T. Indirect immunofluorescence assay for antibody to germ tube of Candida albicans--a new diagnostic test. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Nov;29(11):1007–1010. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen F. Electron microscopic studies of normal visceral epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1967 Aug;17(2):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latta H. The glomerular cappillary wall. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Sep;32(5):526–544. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R. P. Isolation of glomeruli from mammalian kidneys by graded sieving. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;58(2):135–139. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgaard J. O. A new method for the isolation of ultrastructurally preserved glomeruli. Kidney Int. 1976 Mar;9(3):278–285. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. Cytoplasmic antigens unique to the mycelial or yeast phase of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1184-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winner H. I. The transition from commensalism to parasitism. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81(Suppl):62+–62+. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb12835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]