Abstract
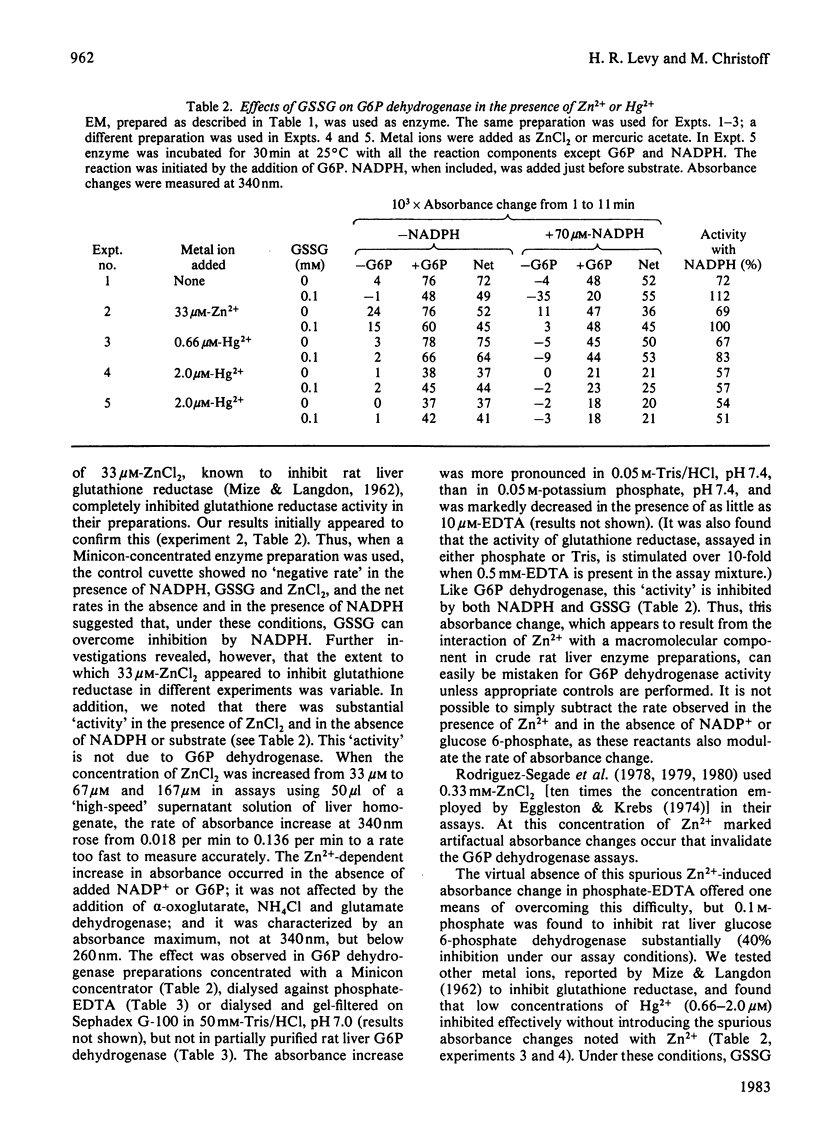
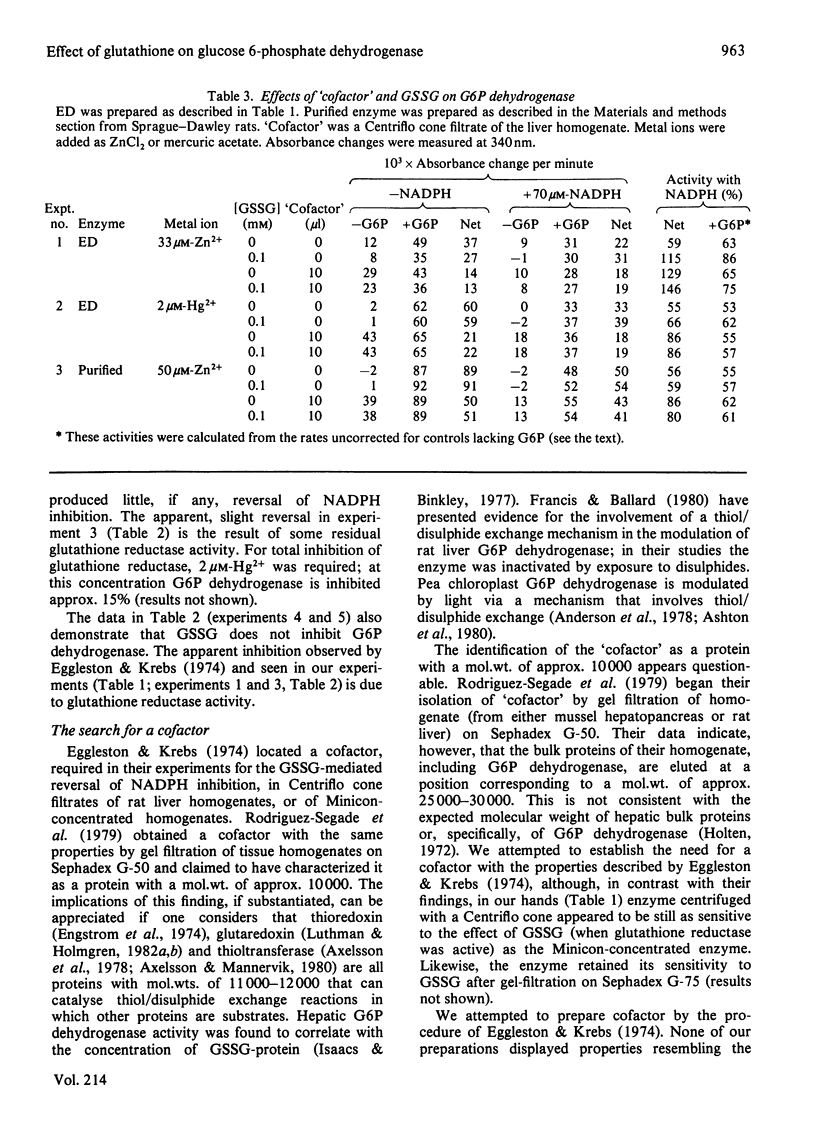
Experiments were undertaken to elucidate the mechanism of the reversal of NADPH inhibition of rat liver glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase by oxidized gluthathione alone and in combination with a putative cofactor described by Eggleston & Krebs [(1974) Biochem. J. 138, 425-435]. Evidence is presented that this reversal is largely an artifact, caused by the incorrect application of a control assay procedure and a spurious effect of Zn2+ (added in order to inhibit glutathione reductase) in crude enzyme solutions. When the proper assay procedure is used and glutathione reductase is inhibited with low concentrations of Hg2+, glutathione addition has no effect on NADPH inhibition of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. No evidence was found for the existence of a cofactor that mediates an effect of glutathione on glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Nehrlich S. C., Champigny M. L. Light modulation of enzyme activity: activation of the light effect mediators by reduction and modulation of enzyme activity by thiol-disulfide exchange. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):601–605. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Brennan T., Anderson L. E. Thioredoxin-like Activity of Thylakoid Membranes: THIOREDOXIN CATALYZING THE REDUCTIVE INACTIVATION OF GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE OCCURS IN BOTH SOLUBLE AND MEMBRANE-BOUND FORM. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):605–608. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Eriksson S., Mannervik B. Purification and characterization of cytoplasmic thioltransferase (glutathione:disulfide oxidoreductase) from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2978–2984. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Mannervik B. General specificity of cytoplasmic thioltransferase (thiol:disulfide oxidoreductase) from rat liver for thiol and disulfide substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):324–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg I., Mannervik B. Purification and characterization of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFlora A., Morelli A., Benatti U., Giuliano F. An improved procedure for rapid isolation of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jul;169(1):362–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. Regulation of the pentose phosphate cycle. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):425–435. doi: 10.1042/bj1380425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström N. E., Holmgren A., Larsson A., Söderhäll S. Isolation and characterization of calf liver thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Ballard F. J. Enzyme inactivation via disulphide-thiol exchange as catalysed by a rat liver membrane protein. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):581–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1860581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi B., Flynn T. G., Levy H. R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Isolation and sequence of a peptide containing an essential lysine. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6415–6420. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten D. Relationships among the multiple molecular forms of rat liver glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 7;268(1):4–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J., Binkley F. Glutathione dependent control of protein disulfide-sulfhydryl content by subcellular fractions of hepatic tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):192–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. S., Jandl J. H. Effects of sulfhydryl inhibition on red blood cells. 3. Glutathione in the regulation of the hexose monophosphate pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4243–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman M., Holmgren A. Glutaredoxin from calf thymus. Purification to homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6686–6690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman M., Holmgren A. Rat liver thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6628–6633. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIZE C. E., LANGDON R. G. Hepatic glutathione reductase. I. Purification and general kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1589–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. M. The role of glutathione in rat adipocyte pentose phosphate cycle activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Mar;207(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevaldine B. H., Hyde C. M., Levy H. R. Mammary glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Molecular weight studies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Wice B. M., Kennell D. The pentose cycle. Control and essential function in HeLa cell nucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5616–5626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Segade S., Freire M., Carrion A. Regulation of the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate cycle in mussels. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):577–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1700577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Segade S., Carrión A., Freire M. Isolation and purification of a regulating cofactor of the pentose-phosphate pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90956-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreve D. S., Levy H. R. Kinetic mechanism of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from the lactating rat mammary gland. Implications for regulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2670–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Spivey H. O., Katz A. J. Rat liver cytoplasmic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Steady-state kinetic properties and circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):862–867. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate in the cytoplasm of rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):609–619. doi: 10.1042/bj1150609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe A., Taketa K., Kosaka K. Glutathione-dependent interconversion of microheterogeneous forms of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in rat liver. J Biochem. 1972 Sep;72(3):695–701. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


