Abstract
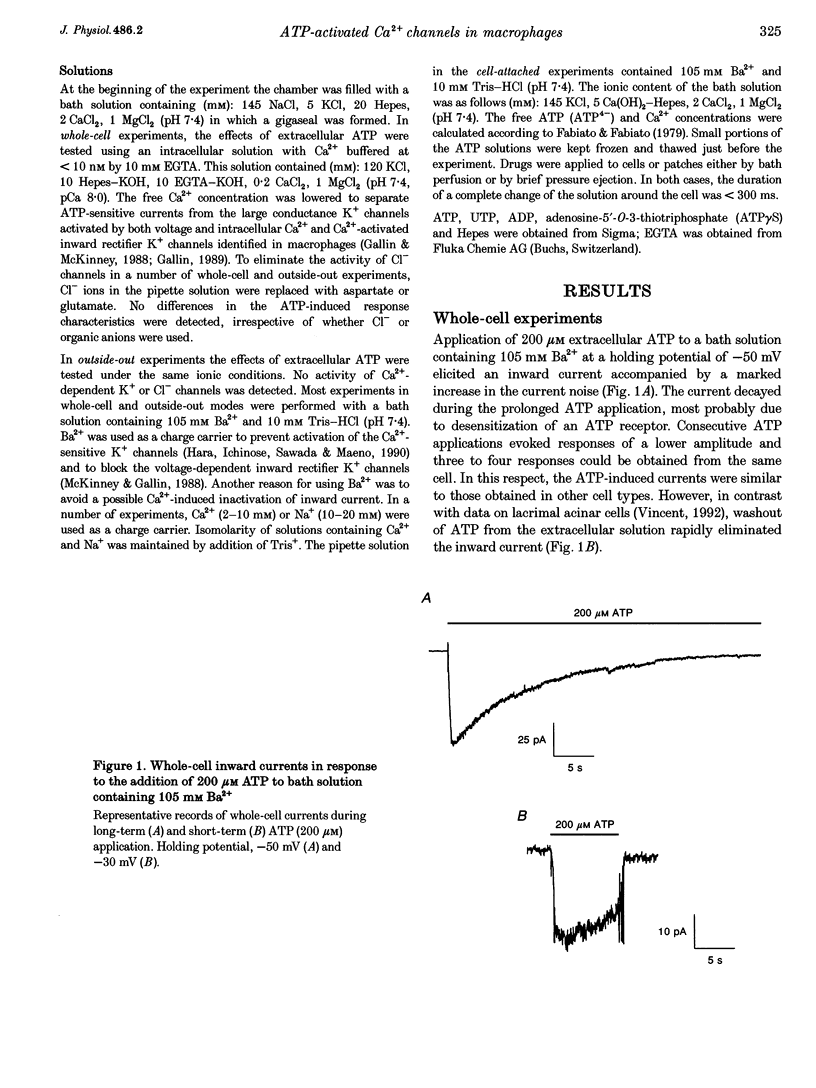
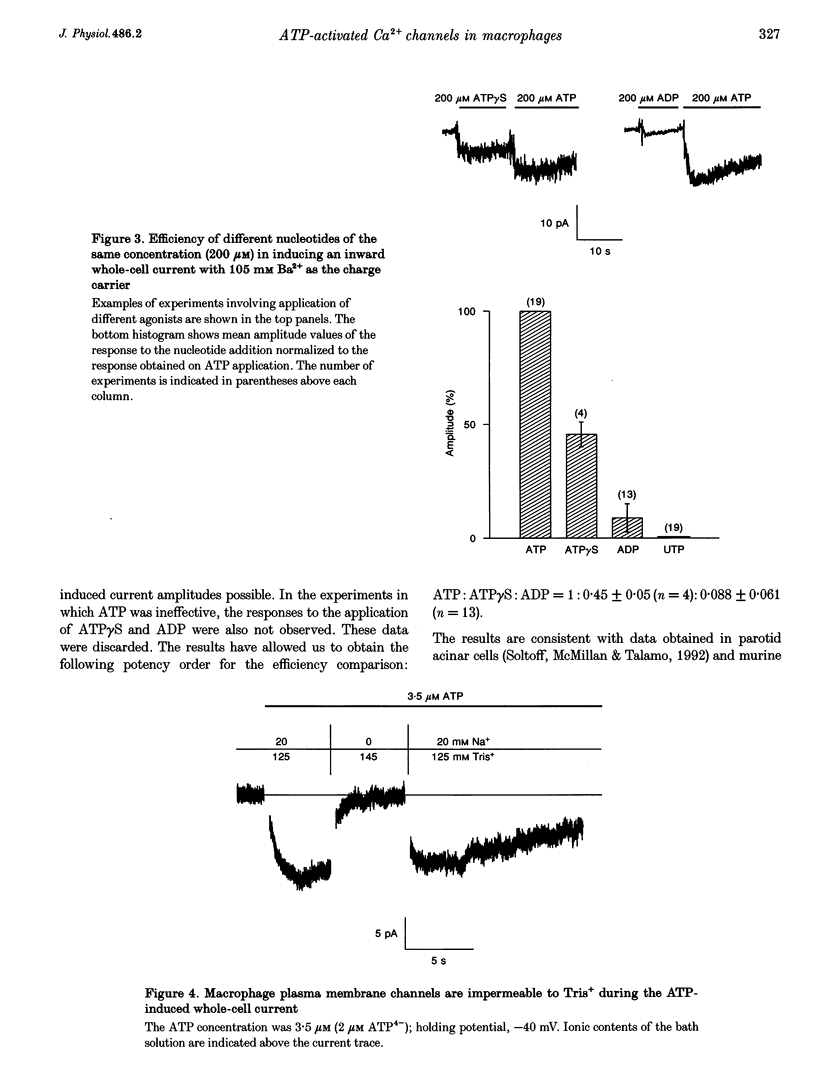
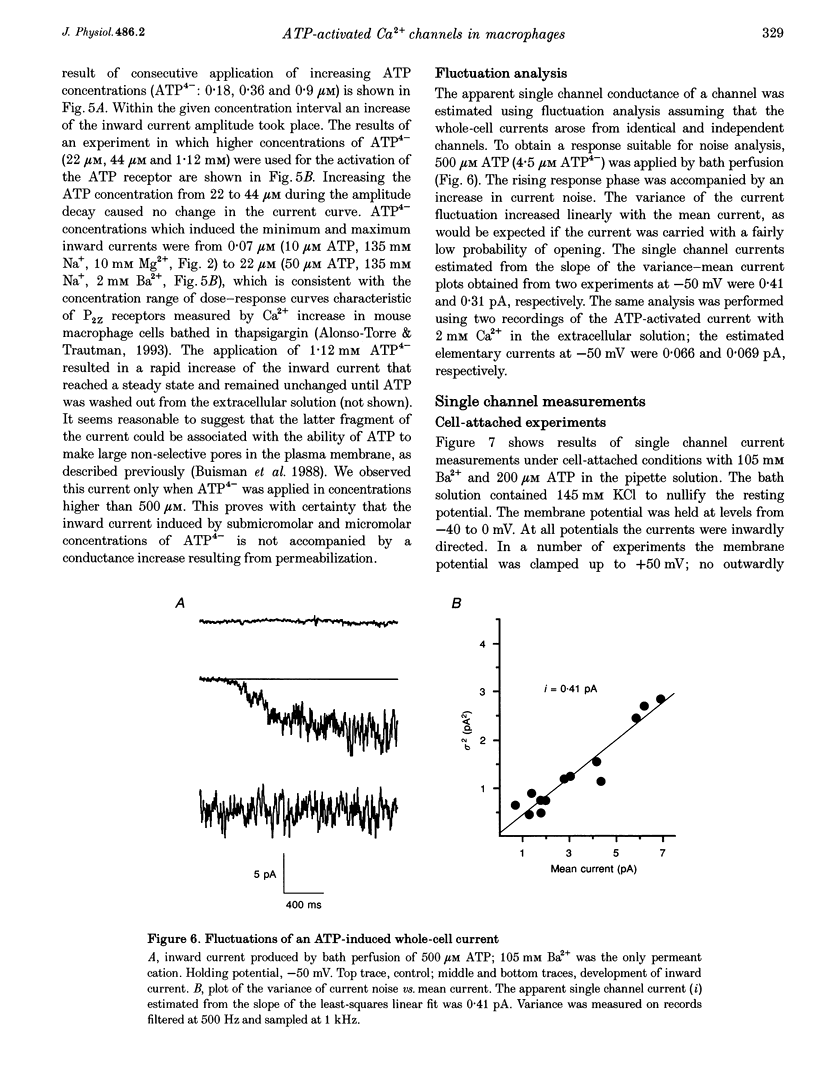
1. To study mechanisms of receptor-operated Ca2+ influx in non-excitable cells, membrane currents of rat peritoneal macrophages were recorded using whole-cell cell-attached and outside-out configurations of the patch clamp technique. Under whole-cell recording conditions, ATP applied in micromolar concentrations elicited an inward current response when the bath solution contained Ba2+, Ca2+ or Na+ as the only permeant cations. 2. Increasing the Mg2+ concentration had an inhibitory effect on the ATP-induced inward current indicating that the active form of ATP responsible for the cation entry is ATP4-. The nucleotide potency order was ATP > ATP gamma S > ADP. UTP was completely ineffective (n = 19). The data obtained are consistent with the ATP receptor being of the P2Z type. 3. The macrophage plasma membrane was impermeable to Tris+ during the ATP-induced current at ATP4- concentrations varying from 0.07 to 500 microM. At higher concentrations, ATP produced a large inward steady-state current, which could be attributed to membrane permeabilization. 4. Activity of single channels was recorded when ATP was applied to the external surface of the patch membrane both in cell-attached and outside-out experiments. A specific property of the channels appeared to be the existence of at least four conductance sublevels. With 105 mM Ba2+ as the permeant cation, the conductance sublevels were 3.5, 7, 10 and 15 pS. With 10 mM Ca2+ the sublevel conductances were equal to 4, 9, 13 and 17 pS. 5. The unitary conductance estimated from the whole-cell current noise analysis (3.5-4.5 pS for 105 mM Ba2+) was significantly lower than that obtained from single channel measurements at the main (3rd) current level, but it was very close to the conductance of the minimum (1st) level. 6. Extrapolated reversal potential values estimated from current-voltage curves for predominant conductance levels were equal to +40 and +26 mV for 105 mM Ba2+ and 10 mM Ca2+, respectively. The permeability ratios fell in the sequence: PCa:PBa:PK = 71.:29:1. Thus, ATP-activated channels in the macrophage membrane are rather selective for divalent vs. monovalent cations, with the predominant permeability being for Ca2+.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso-Torre S. R., Trautmann A. Calcium responses elicited by nucleotides in macrophages. Interaction between two receptor subtypes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18640–18647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: concentration dependence and kinetics. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Pharmacology and electrophysiology of ATP-activated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisman H. P., Steinberg T. H., Fischbarg J., Silverstein S. C., Vogelzang S. A., Ince C., Ypey D. L., Leijh P. C. Extracellular ATP induces a large nonselective conductance in macrophage plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7988–7992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. Ion channel subconductance states. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01869609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D. An ATP-sensitive conductance in single smooth muscle cells from the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:361–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Evidence for a Ca-activated inwardly rectifying K channel in human macrophages. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):C77–C85. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.1.C77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., McKinney L. C. Patch-clamp studies in human macrophages: single-channel and whole-cell characterization of two K+ conductances. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(1):55–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01871932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geletyuk V. I., Kazachenko V. N. Single Cl- channels in molluscan neurones: multiplicity of the conductance states. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01871605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara N., Ichinose M., Sawada M., Maeno T. Extracellular ATP activates Ca2(+)-dependent K+ conductance via Ca2+ influx in mouse macrophages. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1990;97(3):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(90)90633-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Obukhov A. G. Cationic channels activated by extracellular ATP in rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 1988 Dec;27(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Ritchie A. K. Multiple conductance levels of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel in GH3 cells. J Membr Biol. 1990 Nov;118(2):171–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01868474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. Y., Lai F. A., Rousseau E., Jones R. V., Meissner G. Multiple conductance states of the purified calcium release channel complex from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82835-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Receptor-activated single channels in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10479–10483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga H., Nishimoto I., Kojima I., Yamashita N., Kurokawa K., Ogata E. Activation of a calcium-permeable cation channel by insulin-like growth factor II in BALB/c 3T3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):C442–C446. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.4.C442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney L. C., Gallin E. K. Inwardly rectifying whole-cell and single-channel K currents in the murine macrophage cell line J774.1. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(1):41–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01871931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Lechleiter J. D., Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Extracellular ATP increases free cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. Differences from phospholipase C-linked receptor agonists. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):291–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Nagy K. Multiple conductance states of the sodium channel and of other ion channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan R. A., Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural localization of nonspecific esterase activity in guinea pig and human monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1089–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A., Inoue K. An ATP-activated conductance in pheochromocytoma cells and its suppression by extracellular calcium. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Inoue K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. ATP-activated single-channel currents recorded from cell-free patches of pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90741-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Matsuki N. Adenosine triphosphate-activated inward current in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat vas deferens. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):644–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00584668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov A. P., Kuryshev Y. A., Kaznacheyeva E. V., Mozhayeva G. N. ATP-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels in rat peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81210-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov A. P., Kuryshev Y. A., Mozhayeva G. N. Multiple conductance levels of calcium-permeable channels activated by epidermal growth factor in A431 carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 9;1145(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90299-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Stevens C. F. Conductance fluctuations and ionic pores in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:345–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus R., Reber B. F., Reuter H. Regulation of bradykinin- and ATP-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3984–3990. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. Extracellular ATP activates receptor-operated cation channels in mouse lacrimal acinar cells to promote calcium influx in the absence of phosphoinositide metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80782-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. The ATP-induced inward current in mouse lacrimal acinar cells is potentiated by isoprenaline and GTP. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:103–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Talamo B. R. ATP activates a cation-permeable pathway in rat parotid acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C934–C940. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P. Cationic channels sensitive to extracellular ATP in rat lacrimal cells. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:313–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watras J., Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated channels in cerebellum: presence of multiple conductance states. J Neurosci. 1991 Oct;11(10):3239–3245. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-10-03239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Chen G., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Permeability and Mg2+ blockade of histamine-operated cation channel in endothelial cells of rat intrapulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:395–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


