Abstract
1. We sought to elucidate the mechanism of the defective inactivation that characterizes sodium channels containing mutations in the cytoplasmic loop between the third and fourth domains (the III-IV linker). Specifically, we measured whole-cell and single-channel currents through wild-type and F1304Q mutant mu 1 rat skeletal muscle Na+ channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. 2. In wild-type channels, inactivation is complete and the faster of two decay components predominates. In F1304Q, inactivation is incomplete; the slow decay component is larger in amplitude and slower than in wild-type. The fraction of non-inactivating current is substantial (37 +/- 2% of peak current at -20 mV) in F1304Q. 3. Cell-attached patch recordings confirmed the profound kinetic differences and indicated that permeation was not altered by the F1304Q mutation. The F1304Q phenotype must be conferred entirely by changes in gating properties and is not remedied by coexpression with the beta 1-subunit. 4. Recovery from inactivation of F1304Q channels is faster than for wild-type channels and three exponentials are required to describe recovery adequately following long (5 s) depolarizations. Thus, there are three inactivated states even in 'inactivation-deficient' F1304Q channels. 5. The steady-state voltage dependence of F1304Q inactivation is right-shifted by 26 +/- 2 mV. 6. A gating model incorporating three inactivated states, all directly accessible from multiple closed states or the open state, was constrained to fit wild-type and F1304Q inactivation (h infinitive) data and repriming data simultaneously. While it was necessary to alter the rate constants entering and exiting all three inactivated states, the model accounted for the F1304Q-induced rightward shift in steady-state inactivation without imposing voltage dependence on the inactivation rate constants. 7. We conclude that the F1304Q mutation in mu 1 sodium channels modifies several inactivation processes simultaneously. The fact that a single amino acid substitution profoundly alters both fast and slow inactivation indicates that these processes share physical determinants in Na+ channels.
Full text
PDF





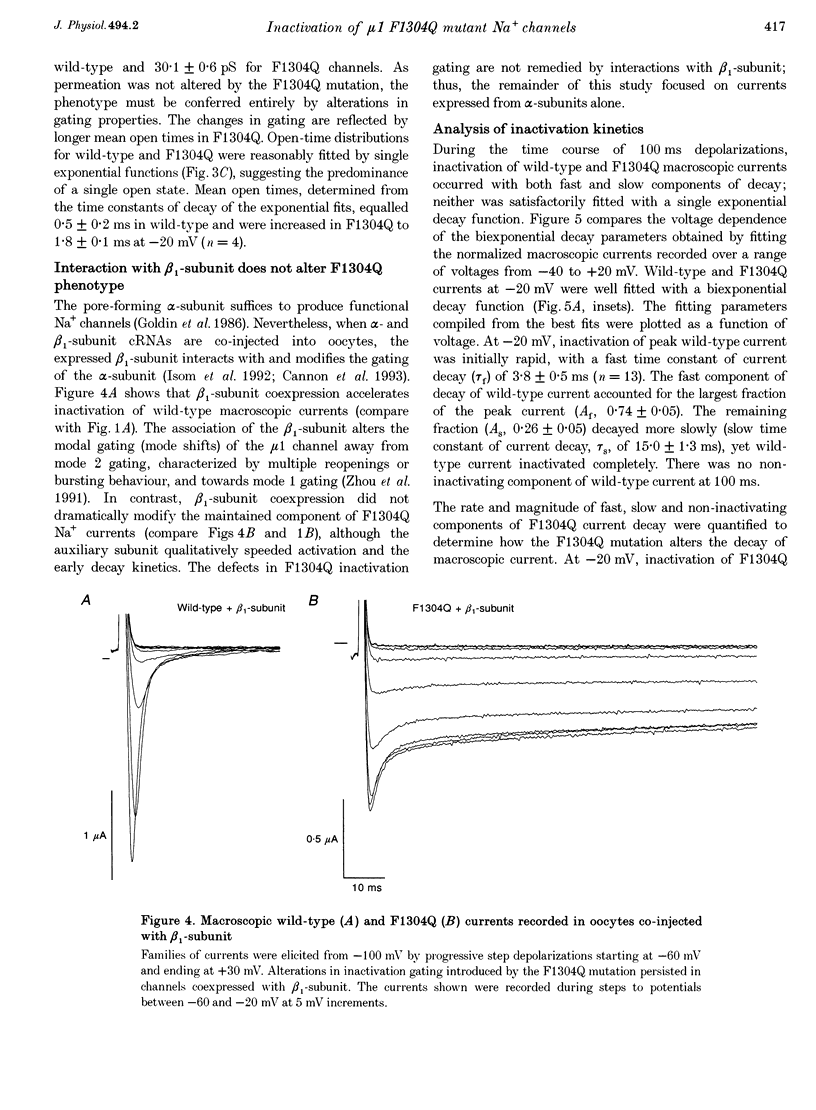

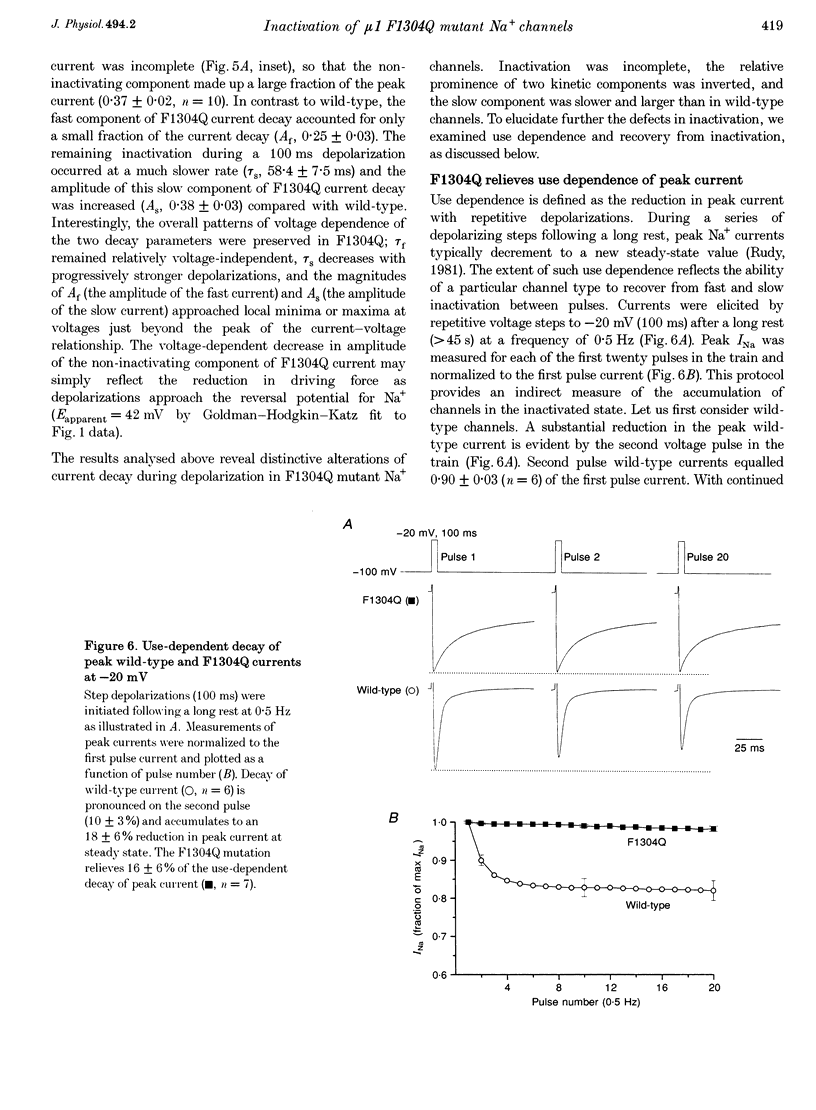










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Cooper E. C., Shenkel S., Correa A. M., James W. M., Ukomadu C., Tomiko S. A. Voltage-sensitive sodium channels: agents that perturb inactivation gating. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:200–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Stevens C. F. Voltage-dependent gating of single sodium channels from mammalian neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):418–431. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00418.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backx P. H., Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):248–251. doi: 10.1126/science.1321496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balser J. R., Nuss H. B., Chiamvimonvat N., Pérez-García M. T., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. External pore residue mediates slow inactivation in mu 1 rat skeletal muscle sodium channels. J Physiol. 1996 Jul 15;494(Pt 2):431–442. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balser J. R., Roden D. M., Bennett P. B. Global parameter optimization for cardiac potassium channel gating models. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):433–444. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82560-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. B., Jr, Makita N., George A. L., Jr A molecular basis for gating mode transitions in human skeletal muscle Na+ channels. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 12;326(1-3):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81752-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E., Fernández J. M. Distribution and kinetics of membrane dielectric polarization. 1. Long-term inactivation of gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):21–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., McClatchey A. I., Gusella J. F. Modification of the Na+ current conducted by the rat skeletal muscle alpha subunit by coexpression with a human brain beta subunit. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):155–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00374974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Snutch T., Lübbert H., Dowsett A., Marshall J., Auld V., Downey W., Fritz L. C., Lester H. A., Dunn R. Messenger RNA coding for only the alpha subunit of the rat brain Na channel is sufficient for expression of functional channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7503–7507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Hille B. Gating of Na channels. Inactivation modifiers discriminate among models. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Feb;89(2):253–274. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Tiedeman A. A., Chen S. F., Brown A. M., Kirsch G. E. Effects of III-IV linker mutations on human heart Na+ channel inactivation gating. Circ Res. 1994 Jul;75(1):114–122. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert T. E., Monette R., Dunn R. J., Drapeau P. Voltage dependencies of the fast and slow gating modes of RIIA sodium channels. Proc Biol Sci. 1994 Jun 22;256(1347):253–261. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1994.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R. Overexcited or inactive: ion channels in muscle disease. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):681–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A. Statistical properties of single sodium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):505–534. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafte D. S., Goldin A. L., Auld V. J., Dunn R. J., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Inactivation of cloned Na channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Oct;96(4):689–706. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Bean B. P. Na+ channels must deactivate to recover from inactivation. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):819–829. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. H., Yue D. T., Rose W. C., Marban E. Sodium channel inactivation from resting states in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:629–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhee J. C., Ragsdale D. S., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. A mutation in segment IVS6 disrupts fast inactivation of sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12346–12350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss H. B., Chiamvimonvat N., Pérez-García M. T., Tomaselli G. F., Marbán E. Functional association of the beta 1 subunit with human cardiac (hH1) and rat skeletal muscle (mu 1) sodium channel alpha subunits expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Dec;106(6):1171–1191. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.6.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. Molecular kinetics of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. Physiol Rev. 1991 Oct;71(4):1047–1080. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.4.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., West J. W., Catterall W. A., Goldin A. L. Amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation: charge neutralizations and deletions in the III-IV linker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10905–10909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Inactivation in Myxicola giant axons responsible for slow and accumulative adaptation phenomena. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:531–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Ricker K., Lehmann-Horn F. Genotype-phenotype correlations in human skeletal muscle sodium channel diseases. Arch Neurol. 1993 Nov;50(11):1241–1248. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540110113011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanley B. E., Hanck D. A., Chay T., Fozzard H. A. Kinetic analysis of single sodium channels from canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):411–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaselli G. F., Chiamvimonvat N., Nuss H. B., Balser J. R., Pérez-García M. T., Xu R. H., Orias D. W., Backx P. H., Marban E. A mutation in the pore of the sodium channel alters gating. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1814–1827. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80358-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela C., Bennett P. B., Jr Gating of cardiac Na+ channels in excised membrane patches after modification by alpha-chymotrypsin. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80465-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Shen J., Splawski I., Atkinson D., Li Z., Robinson J. L., Moss A. J., Towbin J. A., Keating M. T. SCN5A mutations associated with an inherited cardiac arrhythmia, long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):805–811. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Patton D. E., Scheuer T., Wang Y., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E. Two molecular transitions influence cardiac sodium channel gating. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):349–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2540529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J. Y., Potts J. F., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. S., Sigworth F. J. Multiple gating modes and the effect of modulating factors on the microI sodium channel. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90280-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


