Abstract
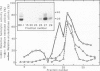
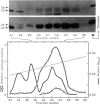
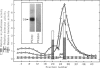
Cytoplasmic granules from cytolytic T-lymphocytes (CTL) contain two proteins which react with the serine esterase-specific affinity label diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP). One of these is a trypsin-like esterase which consists of two disulfide-linked 35-kd subunits. The other consists of a single 29-kd chain. Both molecules are induced concomitantly with cytolytic activity and perforin activity in a CTL-derived T-cell hybrid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borregaard N., Heiple J. M., Simons E. R., Clark R. A. Subcellular localization of the b-cytochrome component of the human neutrophil microbicidal oxidase: translocation during activation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):52–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Effects of N alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethylketone on the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Corthésy P., Cianfriglia M., Silva A., Nabholz M. Hybrids between rat lymphoma and mouse T cells with inducible cytolytic activity. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):170–172. doi: 10.1038/298170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H. Proteinases of Leishmania mexicana and other flagellate protozoa. Parasitology. 1982 Feb;84(1):149–155. doi: 10.1017/s003118200005174x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Corthesy P., Smith K. A., Fiers W., Conzelmann A., Nabholz M. Characterization of soluble factors that induce the cytolytic activity and the expression of T cell growth factor receptors of a T cell hybrid. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):584–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Redelman D., Minning L. L. The requirement for proteinase activity for human lymphocyte-mediated natural cytotoxicity (NK): evidence that the proteinase is serine dependent and has aromatic amino acid specificity of cleavage. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2647–2654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Leib Z., Servadio C. The mechanism of human NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mode of action of surface-associated proteases in the early stages of the lytic reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. How killer cells kill their targets. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1367–1369. doi: 10.1126/science.3485308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Corthésy P., Nabholz M., Tschopp J. Appearance of cytolytic granules upon induction of cytolytic activity in CTL-hybrids. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2533–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Purification and properties of cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat LGL tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty H. R., Hermann W., Dereski W., Frey T., McConnell H. M. Activatable esterase activity of murine natural killer cell--YAC tumour cell conjugates. J Cell Sci. 1984 Dec;72:1–13. doi: 10.1242/jcs.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierzchala P. A., Dorn C. P., Zimmerman M. A new fluorogenic substrate for plasmin. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):555–559. doi: 10.1042/bj1830555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and biochemical and functional characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T-cell granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8629–8633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redelman D., Hudig D. The mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. III. Protease-specific inhibitors preferentially block later events in cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated lysis than do inhibitors of methylation or thiol-reactive agents. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 1;81(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner C. J., Quigley J. P. Detection, identification, and partial characterization of serine proteases and esterases in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 1;122(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekaly R. P., MacDonald H. R., Zaech P., Nabholz M. Cell cycle regulation of cloned cytolytic T cells by T cell growth factor: analysis by flow microfluorometry. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1407–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]