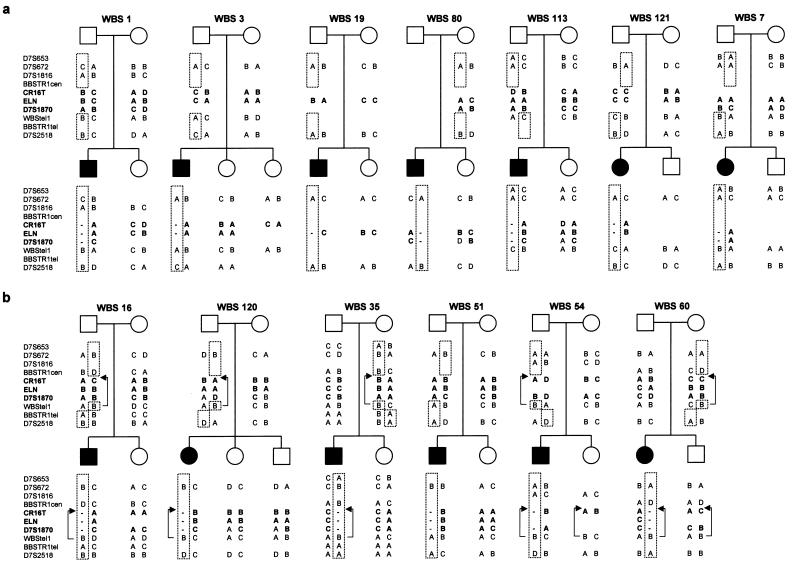
Figure 8.
Haplotype analyses of 13 families with WBS, performed using polymorphic markers centromeric to (D7S653, D7S672, D7S1816, and BBSTR1cen), within (CR16T, ELN, and D7S1870), and telomeric to (WBStel1, BBSTR1tel, and D7S2518) the WBS deleted region. Absence or presence of recombination between centromeric and telomeric markers indicates that the deletion arose as a result of an intra- or interchromosomal recombination event, respectively. In the inverted chromosomes, absence or presence of recombination between centromeric markers and WBStel1 indicates that the deletion arose through a type 1 (patient 51.01) or type 2 (patients 16.01, 120.01, 35.01, 54.01, and 60.01) interchromosomal crossing-over event, respectively (fig. 7b). The brackets encompass the inverted interval with the arrows indicating the position of the WBStel1 marker in chromosomes with an inversion (.11: father, .01: patient, .02/.03: unaffected sibs, and .12: mother).