Abstract
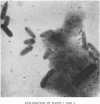
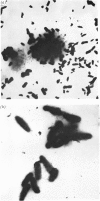
1. The insoluble residue and material present in the aqueous layers resulting from treatment of cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with aqueous phenol were examined. 2. The products (fractions AqI and AqII) isolated from the aqueous layers from the first and second extractions respectively account for approx. 25% and 12% of the cell wall and consist of both lipopolysaccharide and muropeptide. 3. The lipid part of the lipopolysaccharide is qualitatively similar to the corresponding material (lipid A) from other Gram-negative organisms, as is the polysaccharide part. 4. The insoluble residue (fraction R) contains sacculi, which also occur in fraction AqII. On hydrolysis, the sacculi yield glucosamine, muramic acid, alanine, glutamic acid and 2,6-diaminopimelic acid, together with small amounts of lysine, and they are therefore similar to the murein sacculi of other Gram-negative organisms. Fraction R also contains substantial amounts of protein, which differs from that obtained from the phenol layer. 5. The possible association or aggregation of lipopolysaccharide, murein and murein sacculi is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON A. J., CARTER H. E. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LIPID A COMPONENT OF THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:411–418. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson K. J., Eagon R. G. Lysozyme sensitivity of the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Further evidence for the role of the non-peptidoglycan components in cell wall rigidity. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):105–108. doi: 10.1139/m66-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke K., Gray G. W., Reaveley D. A. The cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. General composition. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):749–754. doi: 10.1042/bj1050749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke K., Gray G. W., Reaveley D. A. The extraction of cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with aqueous phenol. Material from the phenol layer. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1050755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHUYSEN J. M., SALTON M. R. Acetylhexosamine compounds enzymically released from Micrococcus lysodeikticus cell walls. I. Isolation and composition of acetylhexosamine and acetylhexosamine-peptide complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 3;40:462–472. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN A. P., OSBORN M. J. O-PHOSPHORYLETHANOLAMINE: A COMPONENT OF LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN CERTAIN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1571–1574. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIS E. W., TINOCO J., OKEY R. A micromethod for fractionation of lipids by silicic acid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1961 Apr;2:100–106. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Westphal O. The significance of enterobacterial mutants for the chemical investigation of their cell-wall polysaccharides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1966 Feb;5(2):198–210. doi: 10.1002/anie.196601981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., ZELEZNICK L. D., HORECKER B. L. LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):783–789. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. An improved method for the detection of N-acetylamino sugars on paper chromatograms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:308–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOCHER A. J., BAYLEY S. T., WATSON R. W. Composition of purified mucopeptide from the wall of Aerobacter cloacae. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Feb;8:89–98. doi: 10.1139/m62-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W. Localization of Somatic Antigen on Gram-Negative Bacteria by Electron Microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):266–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.266-270.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W., Wilkinson J. F. The composition of lipopolysaccharides of Klebsiella aerogenes and Aerobacter cloacae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Knox K. W., Work E. Chemical and biological properties of an extracellular lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli grown under lysine-limiting conditions. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):53–61. doi: 10.1042/bj0990053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., MARTIN H. H. The rigid layer of the cell wall of Escherichia coli strain B. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:158–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PRIMOSIGH J. Biochemical parallels between lysis by virulent phage and lysis by penicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):513–517. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEAT R. W., ROLLINS E. L., LEATHERWOOD J. M., BARNES R. L. Studies on the cell wall of Chromobacterium violaceum: the separation of lipopolysaccharide and mucopeptide by phenol extraction of whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]