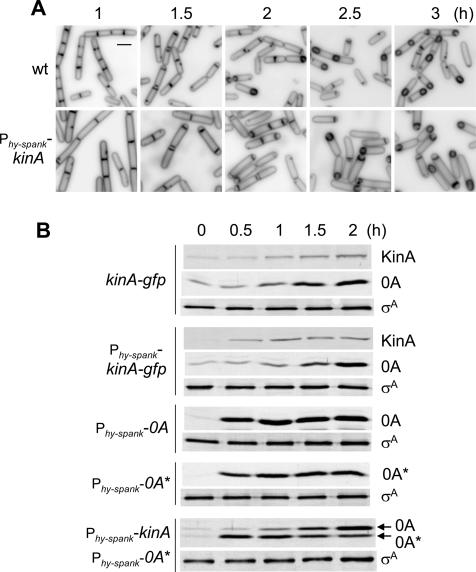
Figure 2.
Comparative timing of sporulation in response to nutrient limitation and induced synthesis of KinA. (A) Sporulation was induced in response to nutrient limitation by cells of the wild-type strain PY79 in SM medium (upper panels) or in response to KinA synthesis by cells of strain MF1887 (Phy-spank-kinA) in CH medium (lower panels). Samples were collected at the indicated times following suspension in SM medium (upper panels) or after the addition of IPTG (lower panels). The cells were treated with the membrane stain FM4-64 and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Bar, 2 μm. (B) Accumulation of KinA and Spo0A in cells of a strain (MF928; kinA-gfp) in which KinA was tagged with GFP and produced under its normal promoter and a strain (MF1996; Phy-spank-kinA-gfp) in which GFP-tagged KinA was produced under the control of an IPTG-inducible promoter. Also shown are the accumulation of Spo0A and Spo0A* in the IPTG-inducible strains MF2001 (Phy-spank-spo0A), MF2146 (Phy-spank-spo0A*), and MF2252 (Phy-spank-kinA, Phy-spank-spo0A*). Samples were collected at the indicated times after suspension in SM medium for the wild-type strain or after the addition of IPTG for all other strains and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GFP antibodies for KinA-GFP, and with anti-Spo0A antibodies for Spo0A and Spo0A*. The anti-σA immunoblot served as a loading control.