Abstract
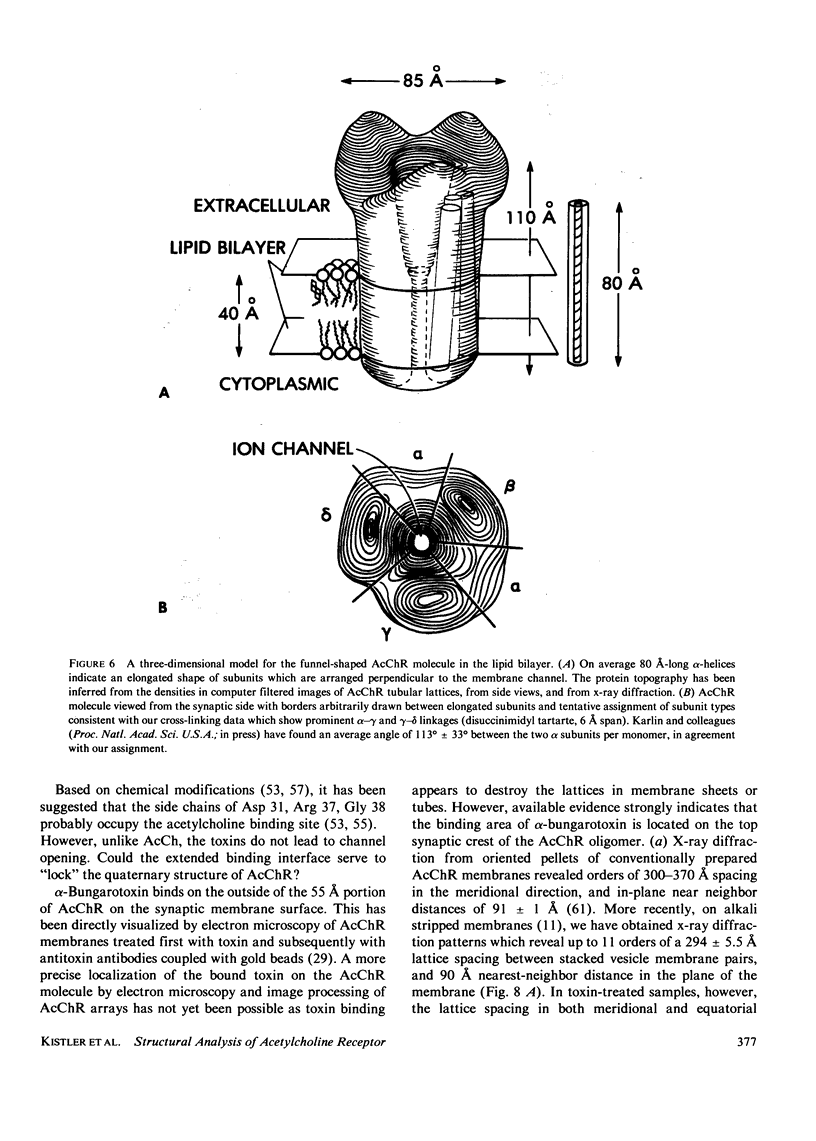
Structural analysis of an acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica leads to a three-dimensional model in which a "monomeric" receptor is shown to contain subunits arranged around a central ionophoretic channel, which in turn traverses the entire 110 A length of the molecule. The receptor extends approximately 15 A on the cytoplasmic side, 55 A on the synaptic side of the membrane. The alpha-bungarotoxin/agonist binding site is found to be approximately 55 A from the entrance to the central gated ion channel. A hypothesis for the mechanism of AcChR is presented which takes into account the structural and kinetic data, which is testable, and which serves as a focus for future studies on the agonist-induced structure change in AcChR.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anholt R., Lindstrom J., Montal M. Functional equivalence of monomeric and dimeric forms of purified acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo californica in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Miledi R., Shipolini R. A. The primary sequences and neuromuscular effects of three neurotoxic polypeptides from the venom of Dendroaspis viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):457–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrantes F. J. Endogenous chemical receptors: some physical aspects. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:287–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovici T., Gitler C. 5-[125I]Iodonaphthyl azide, a reagent to determine the penetration of proteins into the lipid bilayer of biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1484–1489. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L. A morphological study of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata in its membrane environment and in its detergent-extracted purified form. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:313–337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L., Cohen J. B., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Presence of a lattice structure in membrane fragments rich in nicotinic receptor protein from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Benedetti L., Bourgeois J. P., Brisson A., Cartaud J., Devaux P., Grünhagen H., Moreau M., Popot J. L., Sobel A. Some structural properties of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane environmental relevant to its function as a pharmacological receptor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:211–230. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Vincent J. P., Kopeyan C., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. Structure-function relationship in the binding of snake neurotoxins to the torpedo membrane receptor. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2081–2091. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Bromoacetylcholine as an affinity label of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91661-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., McNamee M. G. Independent activation of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica at two sites. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):890–895. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. An analysis of the dose-response relationship at voltage-clamped frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:421–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y., Cohen J. B., Changeux J. P. X-ray diffraction study of membrane fragments rich in acetylcholine receptor protein prepared from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):130–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80910-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J., Blanchard S. G., Wu W., Miller J., Strader C. D., Hartig P., Moore H. P., Racs J., Raftery M. A. Purification of Torpedo californica post-synaptic membranes and fractionation of their constituent proteins. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):667–677. doi: 10.1042/bj1850667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Racker E. Reconstitution of carbamylcholine-dependent sodium ion flux and desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6660–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):165–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Paraschos A., Martinez-Carrion M. Reconstitution of functional membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from isolated Torpedo californica receptor protein and electroplax lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Disulfide bond cross-linked dimer in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):692–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Changeux J. P. Reconstitution of a chemically excitable membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Valderrama R. Facets of the structures of acetylcholine receptors from Electrophorus and Torpedo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:203–210. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M. Crystalline arrays of membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3678–3682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Heuser J. E., Stroud R. M. Protease effects on the structure of acetylcholine receptor membranes from Torpedo californica. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):823–838. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Stroud R. M. Immunospecific identification and three-dimensional structure of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Anholt R., Einarson B., Engel A., Osame M., Montal M. Purification of acetylcholine receptors, reconstitution into lipid vesicles, and study of agonist-induced cation channel regulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8340–8350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Francy M. Acetylcholine receptors and myasthenia gravis: the effect of antibodies to eel acetylcholine receptors on eel electric organ cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977;15:119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Gullick W., Conti-Tronconi B., Ellisman M. Proteolytic nicking of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4791–4795. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C., Anraku M. Permeability of the endplate membrane activated by acetylcholine to some organic cations. J Neurobiol. 1977 Mar;8(2):173–184. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Hartig P. R., Raftery M. A. Correlation of polypeptide composition with functional events in acetylcholine receptor-enriched membranes from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6265–6269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. M., Holladay L. A., Puett D., Brady R. N. On the conformation of the acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo nobiliana. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80832-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Krodel E. K., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):690–694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel E., Potter L. T. Ultrastructure of isolated membranes of Torpedo electric tissue. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):508–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. J., Klymkowsky M. W., Agard D. A., Stroud R. M. Structural studies of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):635–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E., Hess G. P. Characterization of calcium-binding sites of the purified acetylcholine receptor and identification of the calcium-binding subunit. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3818–3825. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sator V., Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Calvo-Fernandez P., Martinez-Carrion M. Pyrenesulfonyl azide: a marker of acetylcholine receptor subunits in contact with membrane hydrophobic environment. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1200–1206. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebler W., Hucho F. Membranes rich in acetylcholine receptor: characterization and reconstitution to excitable membranes from exogenous lipids. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Study of membrane permeability changes by fluctuation analysis. Nature. 1977 Dec 1;270(5636):391–396. doi: 10.1038/270391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. B., Revel J. P., Raftery M. A. Demonstration of the transmembrane nature of the acetylcholine receptor by labeling with anti-receptor antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):499–510. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Raftery M. A. Topographic studies of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor subunits as a transmembrane complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Agard D. A. Structure determination of asymmetric membrane profiles using an iterative Fourier method. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):495–512. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85319-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrab-Hazdai R., Geiger B., Fuchs S., Amsterdam A. Localization of acetylcholine receptor in excitable membrane from the electric organ of Torpedo: Evidence for exposure of receptor antigenic sites on both sides of the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2497–2501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A., Hudson R. A. Structure and function of snake venom curarimimetic neurotoxins. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;14(4):710–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. I. Binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin in the absence of effector. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. II. Effect of cholinergic agonists and antagonists on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):15–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise D. S., Karlin A., Schoenborn B. P. An analysis by low-angle neutron scattering of the structure of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica in detergent solution. Biophys J. 1979 Dec;28(3):473–496. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85194-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Raftery M. Ligand binding sites and subunit interactions of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3598–3604. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Quantitation of cation transport by reconstituted membrane vesicles containing purified acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]