Abstract
1. The time dependence of the increase in amplitude (facilitation) of a second end-plate potential (e.p.p.) elicited within 10-100 msec of a preceding e.p.p. was examined at neuromuscular junctions in sartorius muscles of toads. Facilitation was defined by two characteristics, initial facilitation and the time constant of its exponential decay.
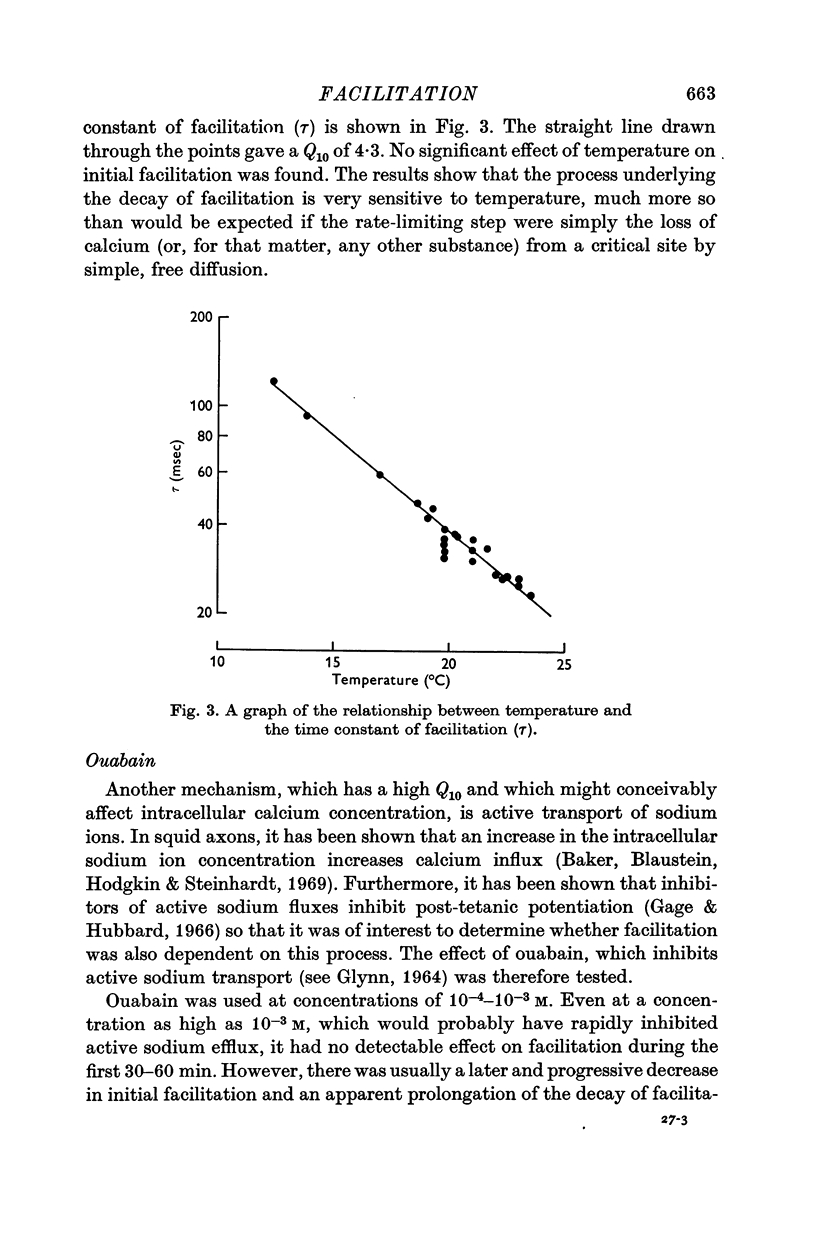
2. The time constant of decay of facilitation was longer at lower temperatures and the Q10 was 4·3 in the range 10-25° C. There was no significant effect of temperature on initial facilitation.
3. Ouabain (10-4-10-3 M), lithium substitution for sodium, sodium azide (5 mM) and N-ethylmaleimide (NEM, 0·1 mM) initially had no effect on initial facilitation or the decay of facilitation. After some time, they all caused a longer time constant of decay of facilitation and a depression of initial facilitation.
4. It was concluded that the decay of facilitation is not directly dependent on active transport of sodium ions, calcium efflux, ATP-dependent movements of calcium or mitochondrial uptake of calcium following an action potential.
5. Ouabain, lithium, sodium azide, and NEM all caused an increase in transmitter release. This effect, and the late effects on facilitation, were thought to be due to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration in nerve terminals.
6. No relationship was found between the quantal content of e.p.p.s (range, 0·8-100) and initial facilitation, or the time constant of decay of facilitation.
7. Substitution of strontium for calcium ions caused a marked prolongation of the time constant of decay of facilitation, and a depression of initial facilitation.
8. The results were consistent with the hypothesis that the time constant of decay of facilitation is related to the rate of disappearance of an `active' complex of calcium (CaA) which, of itself, is not sufficient for transmitter release. It is suggested that an action potential produces CaA which decays with the time constant of facilitation and CaS, a short-life complex of calcium which decays with the time constant of the phasic release of transmitter. The release of transmitter is proportional to some function of [CaA] and [CaS].
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balnave R. J., Gage P. W. Temperature sensitivity of the time course of facilitation of transmitter release. Brain Res. 1970 Jul 14;21(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blioch Z. L., Glagoleva I. M., Liberman E. A., Nenashev V. A. A study of the mechanism of quantal transmitter release at a chemical synapse. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):11–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloedel J., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release at the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):49–50. doi: 10.1038/212049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Schmidt R. F. Potential changes recorded from the frog motor nerve terminal during its activation. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;287(1):56–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00362454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmody J. J., Gage P. W. Lithium stimulates secretion of acetylcholine in the absence of extracellular calcium. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 28;50(2):476–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):553–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Miledi R., Rahamimoff R. Strontium and quantal release of transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):267–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Hubbard J. I. An investigation of the post-tetanic potentiation of end-plate potentials at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):353–375. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I., SCHMIDT R. F. An electrophysiological investigation of mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:145–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. The effect of temperature change upon transmitter release, facilitation and post-tetanic potentiation. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):591–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M., Smolinsky A., Lass Y. Post-tetanic potentiation and facilitation do not share a common calcium-dependent mechanism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio244155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. PRESYNAPTIC AND POST-SYNAPTIC EVENTS DURING POST-TETANIC POTENTIATION AND FACILITATION IN THE AVIAN CILIARY GANGLION. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:17–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C. Neuromuscular facilitation with low-frequency stimulation and effects of some drugs. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;32(5):785–792. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.5.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. The relation between quantum content and facilitation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):593–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri U., Rahamimoff R. Activation of transmitter release by strontium and calcium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):709–726. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. The action of calcium on neuronal synapses in the squid. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):473–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz C. L. Crayfish neuromuscular junction: facilitation with constant nerve terminal potential. Experientia. 1972 Sep 15;28(9):1035–1036. doi: 10.1007/BF01918655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R. A dual effect of calcium ions on neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):471–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D. Sodium-induced efflux of calcium from brain microsomes. Biphasic effect of sulphydryl reagents. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. Post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):121–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Electrical changes in pre- and postsynaptic axons of the giant synapse of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1181–1193. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Carlen P. L., Kushnir M., Kosower E. M. Effect of the thiol-oxidizing agent, diamide, on acetylcholine release at the frog endplate. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 22;233(38):120–121. doi: 10.1038/newbio233120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


