Abstract
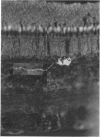
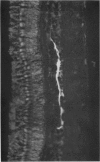
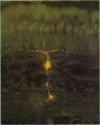
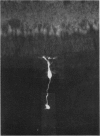
1. Intracellular recordings were made from various types of cells in the isolated goldfish retina, and Procion Yellow was injected from the recording pipette in order to identify histologically the structure recorded. The dye diffused and stained the cell body and processes down to the fine branches.
2. S-potentials were identified as coming from the external horizontal cells and from the internal horizontal cells. Both L- and C-type S-potentials were found in both regions, and no histological differences were seen in cells giving these two types of responses. S-potentials recorded from the external horizontal cells showed less spatial summation than those recorded from the internal horizontal cells.
3. Bipolar cell responses consisted of sustained potentials associated with an antagonistic centre-surround type receptive field (on-centre, off-surround or vice versa). Spike activity was not observed in bipolar cells.
4. Amacrine cells responded with transient depolarization both at the beginning and at the end of illumination. They sometimes showed spike activity. The amplitude of on- and off-depolarization showed slight dependence on stimulus geometry but a distinct centre-surround organization was not observed.
Full text
PDF







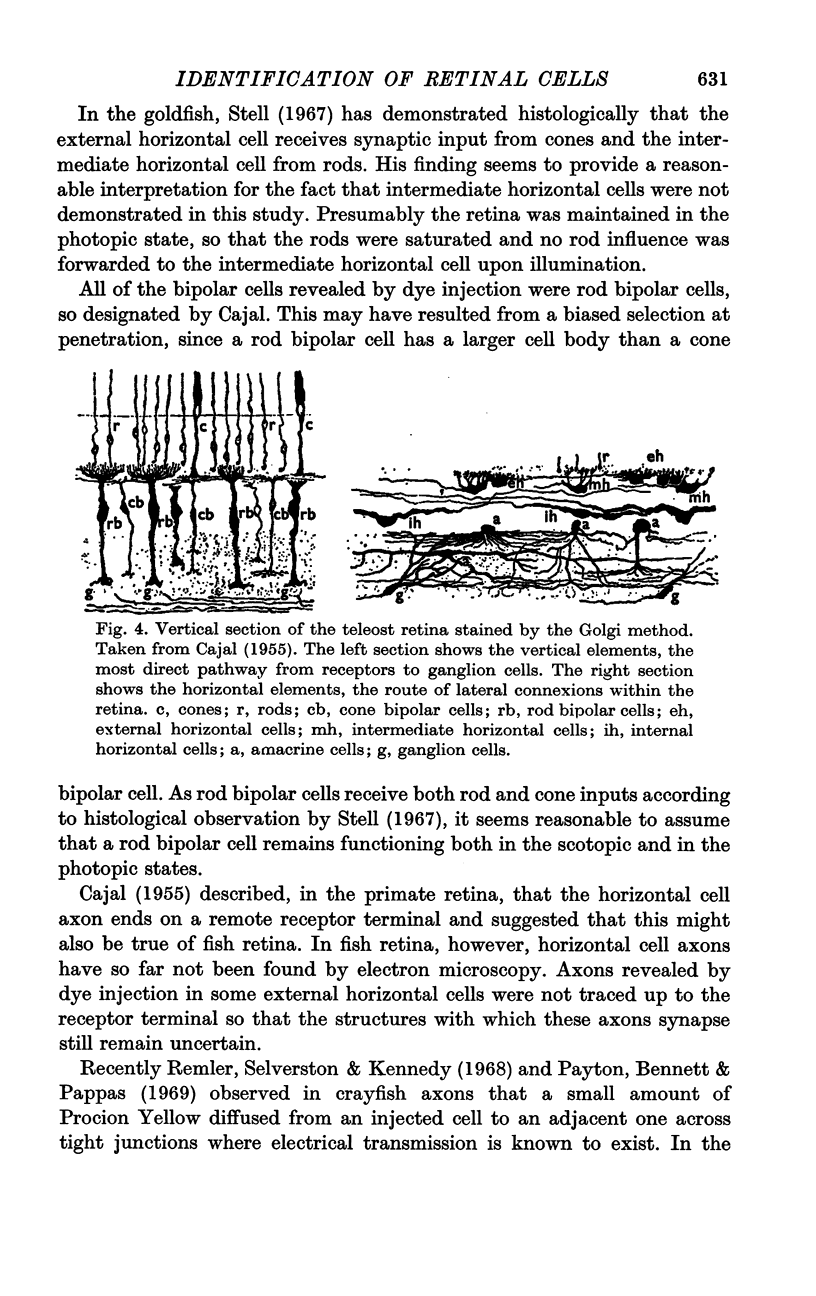







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MACNICHOL E. J., SVAETICHIN G. Electric responses from the isolated retinas of fishes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 2):26–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K. I., Rushton W. A. The generation and spread of S-potentials in fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):437–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OIKAWA T., OGAWA T., MOTOKAWA K. Origin of so-called cone action potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jan;22(1):102–111. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payton B. W., Bennett M. V., Pappas G. D. Permeability and structure of junctional membranes at an electrotonic synapse. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1641–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remler M., Selverston A., Kennedy D. Lateral giant fibers of cray fish: location of somata by dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 11;162(3850):281–283. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3850.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K. The structure and relationships of horizontal cells and photoreceptor-bipolar synaptic complexes in goldfish retina. Am J Anat. 1967 Sep;121(2):401–423. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrophysiological study of the mechanisms subserving color coding in the fish retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:559–566. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S., Dowling J. E. Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. II. Intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):339–355. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada E., Ishikawa T. The fine structure of the horizontal cells in some vertebrate retinae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:383–392. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]