Abstract
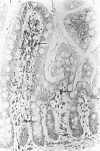
The cellular distribution of immunoreactive interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) was studied in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded normal human tissues from 36 different organs. These samples were drawn from over 300 individuals none of whom had evidence of viral infection. Tissue histiocytes from all organs in the body, with the exception of brain and renal cortex and medulla, stained positively for IFN-alpha. Kupffer cells, pulmonary alveolar macrophages and lymph node macrophages were also positive. Parenchymal cells in some other organs also appeared to contain immunoreactive IFN-alpha. These included cuboidal lining cells of the choroid plexus in the brain, thyroid follicular cells, pituitary endocrine cells, adrenocortical cells and parathyroid principal and oxyphil cells. These findings are compatible with previous suggestions that IFN-alpha may be synthesized and released in the absence of viral infection and may thus have a role in normal physiology. The presence of IFN-alpha in most cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system suggests that these cells may play a major part in defence against viral infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belardelli F., Vignaux F., Proietti E., Gresser I. Injection of mice with antibody to interferon renders peritoneal macrophages permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocci V., Muscettola M., Paulesu L., Grasso G. The physiological interferon response. II. Interferon is present in lymph but not in plasma of healthy rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):101–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocci V. Production and role of interferon in physiological conditions. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1981 Feb;56(1):49–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1981.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T., Craig P. H., Menabawey M., Lee C. Alpha interferon in human pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986 Nov;93(11):1145–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1986.tb08635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exley T., Parti S., Barwick S., Meager A. A comparison of the neutralizing properties of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to human interferon alpha. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2277–2280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Meager A. Immunoreactive alpha-interferon in insulin-secreting beta cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1987 Dec 19;2(8573):1423–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Robert N., Buffet-Janvresse C., Rivière Y., Hovanessian A. G. Continuous production of interferon in normal mice: effect of anti-interferon globulin, sex, age, strain and environment on the levels of 2-5A synthetase and p67K kinase. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):711–718. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., Belardelli F., Borghi P., Boraschi D., Gresser I. Correlation between the lipopolysaccharide response of mice and the capacity of mouse peritoneal cells to transfer an antiviral state. Role of endogenous interferon. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1991–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Belardelli F., Maury C., Maunoury M. T., Tovey M. G. Injection of mice with antibody to interferon enhances the growth of transplantable murine tumors. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2095–2107. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho-Yen D. O., Carrington D. Alpha-interferon responses in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with suspected meningitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jan;40(1):83–86. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howatson A. G., Farquharson M., Meager A., McNicol A. M., Foulis A. K. Localization of alpha-interferon in the human feto-placental unit. J Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;119(3):531–534. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., LINDENMANN J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Sep 12;147(927):258–267. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Virtanen I., Hovi T., Secher D. S., Cantell K. Monocyte is the main producer of human leukocyte alpha interferons following Sendai virus induction. Prog Med Virol. 1984;30:78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Chihara K., Shiozawa K., Fujita T., Ikegami H., Koyama S., Kurimoto M. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for alpha-interferon: circulating alpha-interferon-like substance in the plasma of healthy individuals and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):77–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Wagner R. R. Rabbit macrophage interferons. I. Conditions for biosynthesis by virus-infected and uninfected cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):559–577. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Streuli M., Gresser I., Gugenheim J., Blanchard B., Guymarho J., Vignaux F., Gigou M. Interferon messenger RNA is produced constitutively in the organs of normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoumbos N. C., Gascon P., Djeu J. Y., Young N. S. Interferon is a mediator of hematopoietic suppression in aplastic anemia in vitro and possibly in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., Fauve R. M., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Production d'interféron au niveau du macrophage. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Mar;120(3):438–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]