Abstract
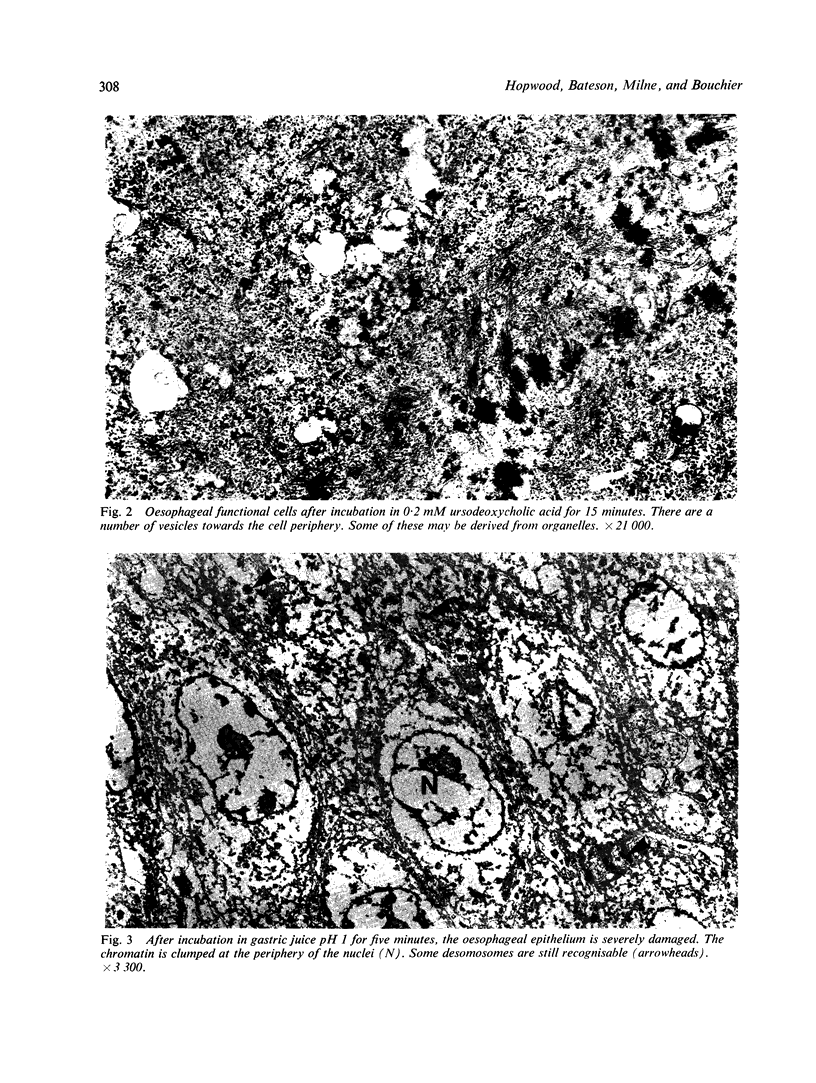
Oesophageal mucosal biopsies were incubated in 20, 0, and 0.2mM solutions of cholic, chenodeoxycholic, ursodeoxycholic, and deoxycholic bile acids. Both conjugated and unconjugated bile acids were studied at pH 1 and 7 singly and in combination. Observations were also made using 0.1 N hydrochloric acid and human gastric juice at pH 1-3 and 7-8. After incubation for up to 15 minutes the mucosa was examined under transmission electron microscopy. We concluded that high and moderate concentration of all the common bile acids damaged the oesophagus irrespective of the pH, that low concentrations of bile acids were damaging only at high acid levels, and that damage to the epithelium did not occur when the pH of the gastric juice had been raised.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN L. M., BAKER L. A. A clinical test for esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1958 May;34(5):760–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateson M. C., Hopwood D., Milne G., Bouchier I. A. Oesophageal epithelial ultrastructure after incubation with gastrointestinal fluids and their components. J Pathol. 1981 Jan;133(1):33–51. doi: 10.1002/path.1711330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Brand D. L., Brown F. C., Castell D. O., Cohen S., Crossley R. J., Pope C. E., 2nd, Winans C. S. Cimetidine in the treatment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux: a double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 2):441–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J. Reflux esophagitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med. 1976 May;136(5):560–566. doi: 10.1001/archinte.136.5.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysenko J. Z., Revel J. P. Experimental manipulation of desmosome structure. Am J Anat. 1973 Aug;137(4):403–421. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001370404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin M. K., Stol D. W., Murphy G. M., Collis J. L. The pattern of bile salt reflux and acid secretion in sliding hiatal hernia. Br J Surg. 1974 Aug;61(8):611–616. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800610806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R., Dronfield M. W., Atkinson M. Cimetidine in treatment of reflux oesophagitis with peptic stricture. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 25;2(6188):472–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6188.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillison E. W., De Castro V. A., Nyhus L. M., Kusakari K., Bombeck C. T. The significance of bile in reflux esophagitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Mar;134(3):419–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. D. Gastroesophageal reflux following gastric operation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1978 Dec;26(6):563–573. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62943-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare A. M., Keighley M. R., Starkey B., Alexander-Williams J. Measurement of bile acids in fasting gastric aspirates: an objective test for bile reflux after gastric surgery. Gut. 1978 Mar;19(3):166–169. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.3.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D., Curtis M., Nicholson G., Milne G. The distribution and mobility of surface anionic groups of normal human oesophageal epithelium following interaction with cationized verritin. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1979;31(3):277–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02889944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGELFINGER F. J. Anticholinergic therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jun 27;268:1454–1457. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196306272682608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebel O. T., Fornes M. F., Castell D. O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux: incidence and precipitating factors. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Nov;21(11):953–956. doi: 10.1007/BF01071906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini C. A., DeMeester T. R., Wernly J. A., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Alkaline gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Surg. 1978 Feb;135(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrokubi R. J., Jeffries G. H. Cimetidine versus antacid in scleroderma with reflux esophagitis. A randomized double-blind controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):691–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. E., 2nd Pathophysiology and diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):445–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees W., Rhodes J. Bile reflux in gastro-oesophageal disease. Clin Gastroenterol. 1977 Jan;6(1):179–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safaie-Shirazi S., DenBesten L., Zike W. L. Effect of bile salts on the ionic permeability of the esophageal mucosa and their role in the production of esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):728–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesdorp E., Bartelsman J., Pape K., Dekker W., Tytgat G. N. Oral cimetidine in reflux esophagitis: a double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):821–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






