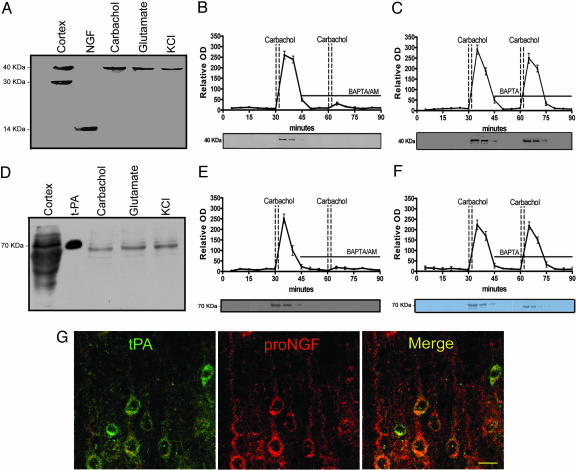
Fig. 1.
Neuronal colocalization and stimulus-coupled release of proNGF and tPA. Western blots demonstrating proNGF (A) and tPA (D) released from cerebral cortex after stimulation (see Materials and Methods). First lane illustrates immunoreactive bands from cortical homogenates. In the second lane, 5 ng mNGF (A) or 3 ng tPA (D) are loaded as control. Time course of proNGF (B) and tPA (E) released from cerebral cortex tissue. Activity-dependent release of neuroactive proteins was induced by two consecutive carbachol stimulations. The presence of the intracellular calcium chelator, BAPTA/AM (10 μM), in the superfusion buffer inhibited the release of proNGF (B) and of tPA (E) but the presence of the extracellular calcium chelator, BAPTA (10 μM), did not affect proNGF (C) or tPA (F) release (mean ± SEM). (G) Localization of tPA (green) and proNGF (red) in cortical pyramidal neurons; colocalization illustrated with merged images (yellow). (Scale bar: 20 μm.)