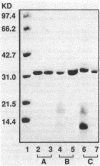
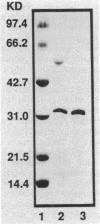
Abstract
Boronic acids are active-site inhibitors of serine beta-lactamases, and a phenylboronic acid-agarose affinity column has been used to purify beta-lactamase from crude cell extracts of several bacterial species. We applied phenylboronic acid-agarose chromatography to the purification of Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase. Two factors interfered with the success of the previously described single-step chromatographic protocol. First, staphylococcal beta-lactamase exhibited non-active-site-mediated adsorption to the agarose used as a support for the meta-aminophenylborate ligand, preventing the recovery of beta-lactamase from the column. Second, the staphylococcal beta-lactamases exhibited low affinity for meta-aminophenylborate with inhibition constants (Kis) ranging from 8.0 x 10(-3) to 20.0 x 10(-3) M. These problems were resolved by modifying the buffers utilized during chromatography and increasing the dimensions of the affinity column, and a two-stage procedure consisting of cation-exchange chromatography followed by affinity chromatography was used to purify each of the four variants of staphylococcal beta-lactamase. The mean specific activities of the purified type A, B, C, and D beta-lactamases were 44.6, 12.2, 10.6, and 30.8 mumol of nitrocefin hydrolyzed per min/mg of protein, respectively. Dimer formation, presumably from intramolecular cysteine-cysteine cross-linking, was observed with the type D beta-lactamase but not with the type A, B, or C enzyme.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of Staphylococcus aureus penicillinase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):197–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1510197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Purification of beta-lactamases by affinity chromatography on phenylboronic acid-agarose. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2210505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. Influence of organic anions on the liberation of penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):748–752. doi: 10.1042/bj1020748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. Liberation of surface-located penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):742–747. doi: 10.1042/bj1020742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton I. E., Cuthbert B. K., Lowe G., Waley S. G. Beta-lactamase inhibitors. The inhibition of serine beta-lactamases by specific boronic acids. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):453–459. doi: 10.1042/bj2510453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East A. K., Dyke K. G. Cloning and sequence determination of six Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamases and their expression in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):1001–1015. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernodle D. S., Classen D. C., Burke J. P., Kaiser A. B. Failure of cephalosporins to prevent Staphylococcus aureus surgical wound infections. JAMA. 1990 Feb 16;263(7):961–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernodle D. S., McGraw P. A., Stratton C. W., Kaiser A. B. Use of extracts versus whole-cell bacterial suspensions in the identification of Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase variants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):420–425. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernodle D. S., Stratton C. W., McMurray L. W., Chipley J. R., McGraw P. A. Differentiation of beta-lactamase variants of Staphylococcus aureus by substrate hydrolysis profiles. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):103–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Waley S. G. Reversible inhibitors of penicillinases. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):197–204. doi: 10.1042/bj1690197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Rosdahl V. T. An unusual "penicillinase plasmid" in staphylococcus aureus; evidence for its transfer under natural conditions. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):1–9. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moult J., Sawyer L., Herzberg O., Jones C. L., Coulson A. F., Green D. W., Harding M. M., Ambler R. P. The crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus at 0.5 nm resolution. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):167–176. doi: 10.1042/bj2250167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mederski-Samoraj B., Foster S. K., Brunton J. L., Harford P. In vitro studies of plasmid-mediated penicillinase from Streptococcus faecalis suggest a staphylococcal origin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):289–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI112289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P., RICHMOND M. H. NATURE AND INTERACTIONS OF THE GENETIC ELEMENTS GOVERNING PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:467–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.467-480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Membrane-bound penicillinases in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4490–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:452–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0880452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. WILD-TYPE VARIANTS OF EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:584–593. doi: 10.1042/bj0940584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Beta-lactamase (Staphylococcus aureus). Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:664–672. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Pain R. H. The mechanism of folding of globular proteins. Suitability of a penicillinase from Staphylococcus Aureus as a model for refolding studies. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):325–330. doi: 10.1042/bj1550325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosdahl V. T. Naturally occurring constitutive -lactamase of novel serotype in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jul;77(1):229–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeg W., Bingöl R., Blobel H. Purification of penicillinase ( -lactamase) and acid phosphatase from Staphylococcus aureus in one procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 12;268(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Kernodle D. S., Eades S. C., Weeks L. S. Evaluation of cefotaxime alone and in combination with desacetylcefotaxime against strains of Staphylococcus aureus that produce variants of staphylococcal beta-lactamase. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;12(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todhunter J. A. Reversible enzyme inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:383–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]