Abstract
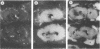
It has been proposed that a bacterium isolated from the gills of shipworms (teredinid mollusks) is, by virtue of its ability both to degrade cellulose and to fix dinitrogen, the symbiont that enables these mollusks to utilize wood as their principal food source. The phylogenetic affiliation of four of these bacteria isolated from wood-boring bivalve mollusks was determined by 16S rRNA sequence analysis by using the reverse transcriptase method with six oligodeoxynucleotide primers. The four bacterial strains tested had indistinguishable 16S rRNA sequences, supporting the previous conclusion, based on phenotypic characterization, that these isolates represent a single species. Evolutionary distance matrix analysis of the RNA sequence indicated that the bacterial symbiont falls within the gamma-3 subdivision of the Proteobacteria and is distinct from other known bacterial genera. In situ localization of the bacterial symbiont in tissue sections of the shipworm Lyrodus pedicellatus was determined by using a 16S rRNA-directed oligodeoxynucleotide hybridization probe specific for the bacterium isolated from shipworm gill tissue. Fluorescence microscopy showed that the specific probe bound to L. pedicellatus tissue at sites coincident with the location of symbiont cells and that it did not bind to other host tissues. This technique provided direct visual evidence that the cellulolytic, nitrogen-fixing bacterial isolates were the symbionts observed within the gill of L. pedicellatus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Krumholz L., Stahl D. A. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):762–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.762-770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. The sequence of the ribosomal 16S RNA from Proteus vulgaris. Sequence comparison with E. coli 16S RNA and its use in secondary model building. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2325–2333. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel D. L., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace B., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A., Felbeck H. Sulfur-oxidizing bacterial endosymbionts: analysis of phylogeny and specificity by 16S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2506–2510. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2506-2510.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Margoliash E. Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):279–284. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Stewart G. C., Hollis M. A., Vold B. S., Bott K. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis ribosomal RNA operon, rrnB. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Earliest phylogenetic branchings: comparing rRNA-based evolutionary trees inferred with various techniques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:825–837. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Phylogenetic analysis using ribosomal RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:793–812. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Meinert F., Wyss U., Ehlers R. U., Stackebrandt E. Development and application of oligonucleotide probes for molecular identification of Xenorhabdus species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.181-186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Characterization of a Yellowstone hot spring microbial community by 5S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1379–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1379-1384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Bratina B. J., Tsuji K., Hanson R. S. Use of oligodeoxynucleotide signature probes for identification of physiological groups of methylotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2858–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2858-2865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterbury J. B., Calloway C. B., Turner R. D. A cellulolytic nitrogen-fixing bacterium cultured from the gland of deshayes in shipworms (bivalvia: teredinidae). Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4618.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R., Ward D. M. Selective Recovery of 16S rRNA Sequences from Natural Microbial Communities in the Form of cDNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1818–1822. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1818-1822.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D., Oyaizu Y., Oyaizu H., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Mitochondrial origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4443–4447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]