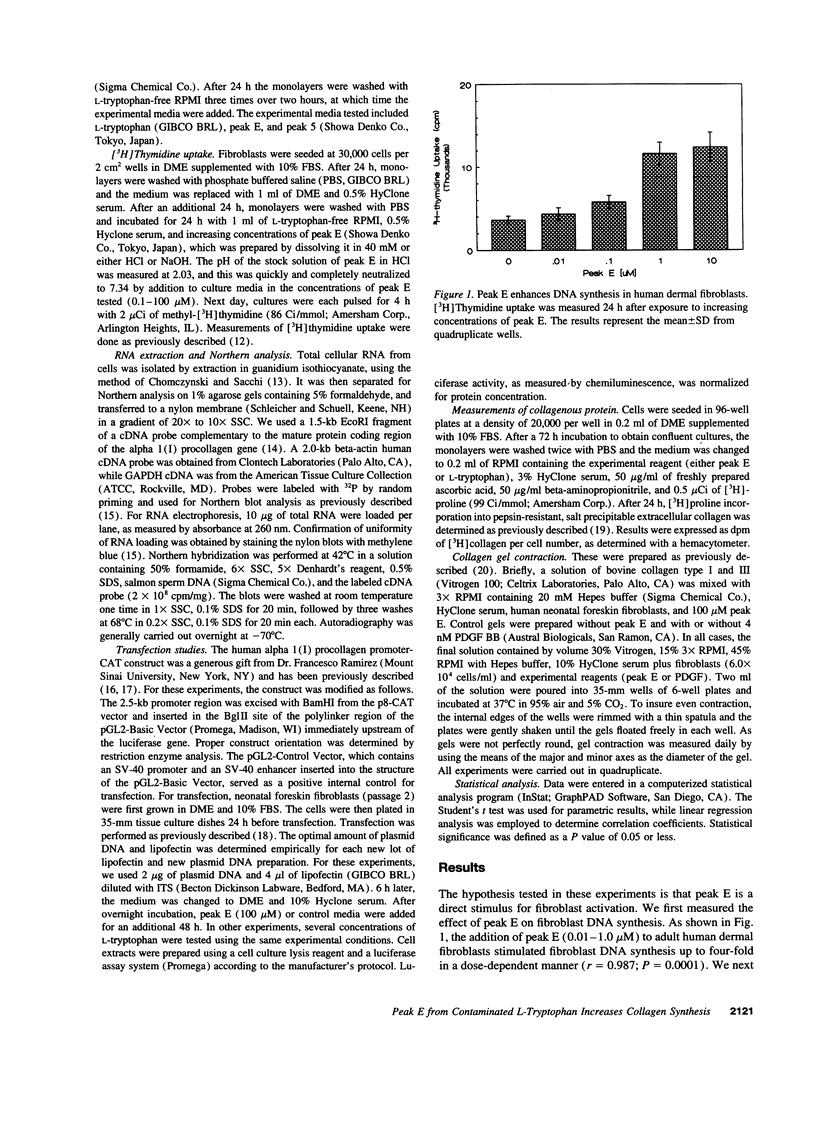
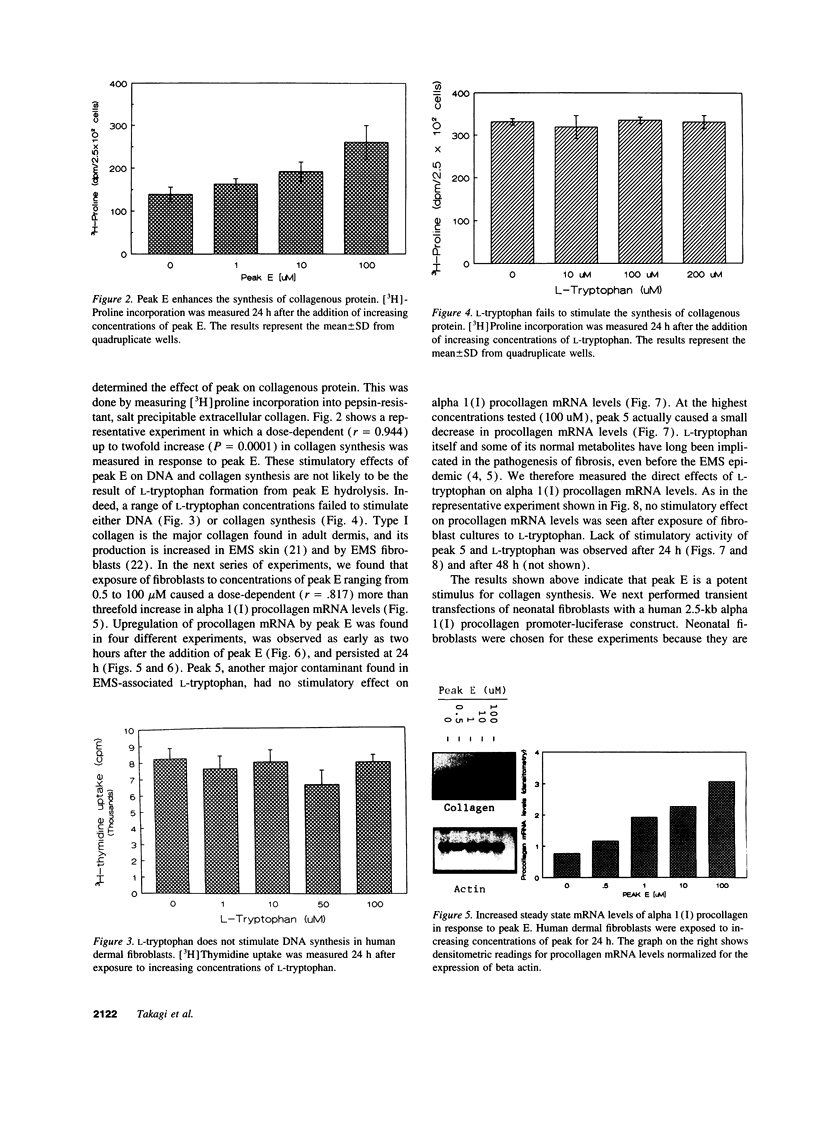
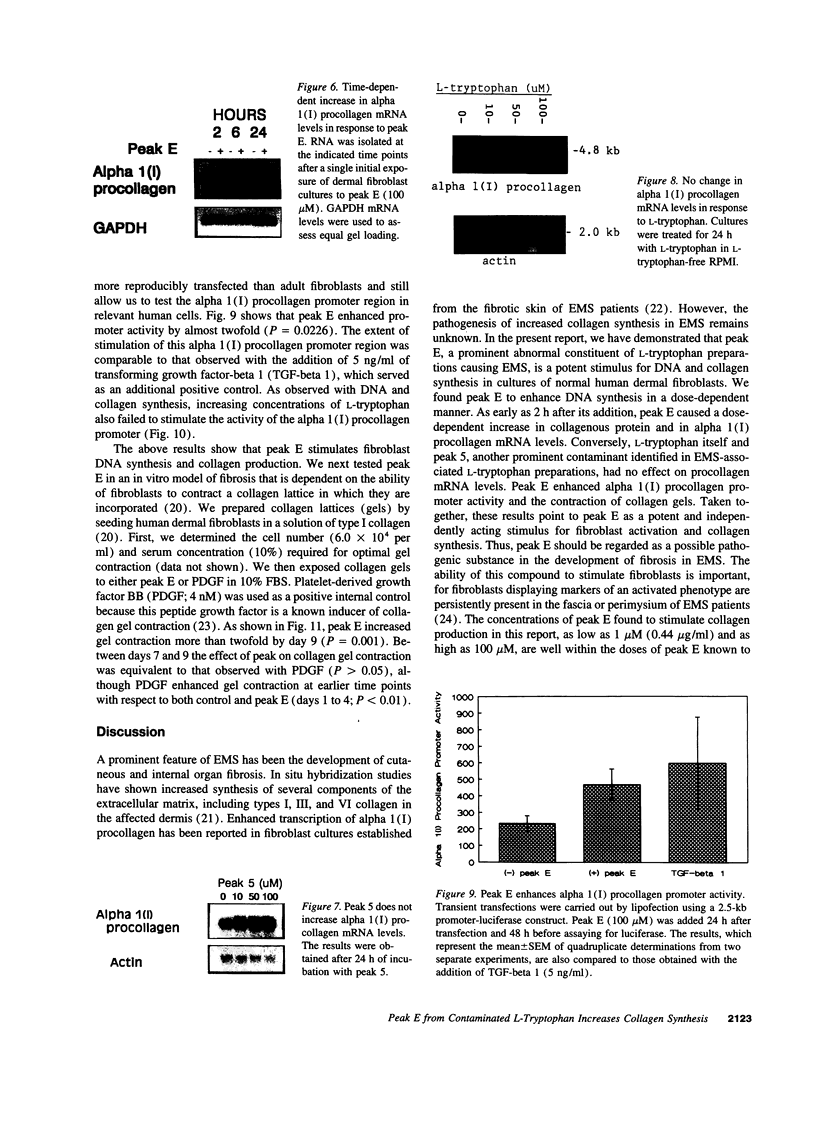
Abstract
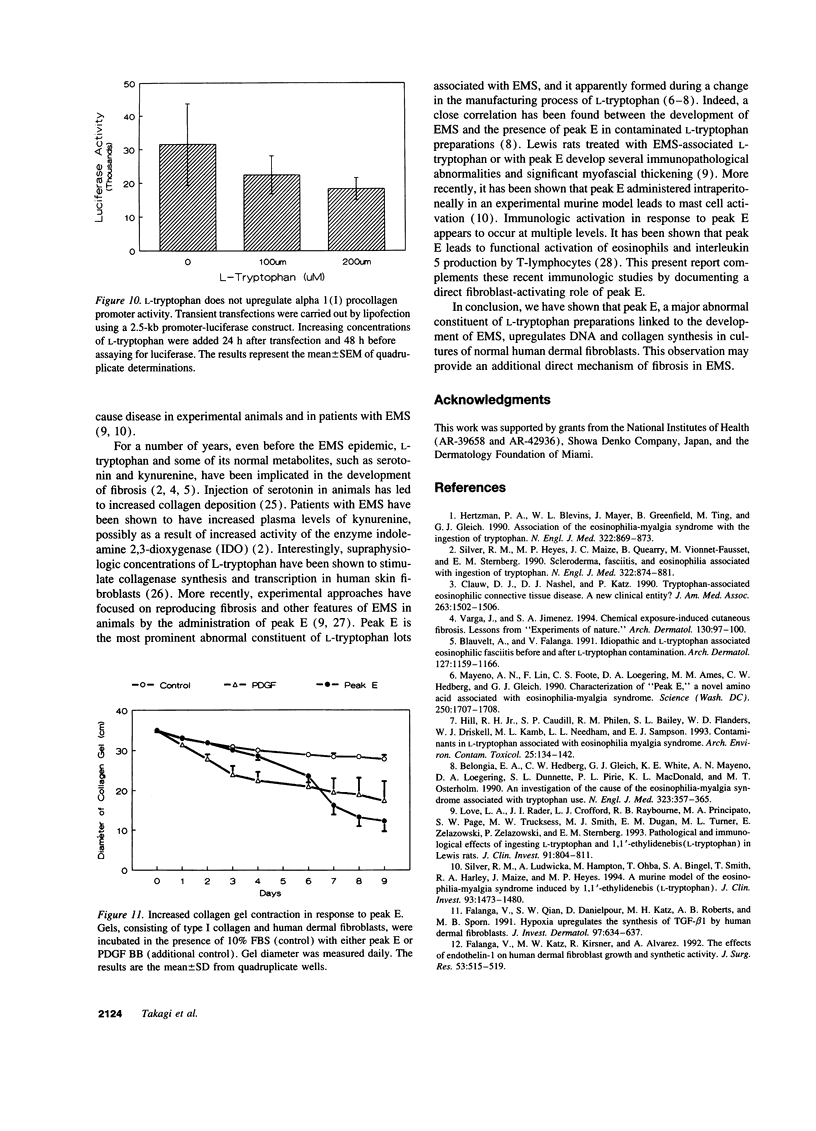
The pathogenesis of the eosinophilia myalgia syndrome (EMS) remains unclear. Several abnormal constituents have been found in the L-tryptophan lots responsible for the illness, particularly, 1,1-ethylidenebis[L-tryptophan], also called peak E or EBT, and 3-phenylamino-alanine or peak 5. However, the role of these contaminants in the pathogenesis of EMS and in the development of fibrosis is unknown. We now report that peak E, a dimer of L-tryptophan, is a potent stimulus for human dermal fibroblast DNA and collagen synthesis. Peak E (0.1-1.0 microM) increased DNA synthesis up to four-fold (P = 0.0001) in a dose-dependent manner (r = 0.987). When added to monolayer cultures for 2 to 24 h, peak E (0.5 to 100 microM) caused a progressive, more than threefold increase in alpha 1(I) procollagen mRNA levels and collagenous protein. No increase in procollagen mRNA levels was found after the addition of another major L-tryptophan contaminant, peak 5, or with L-tryptophan itself. Transient transfection with a 2.5-kb alpha 1(I) procollagen promoter-luciferase construct showed that peak E causes a twofold upregulation of promoter activity (P = 0.022). Contraction of collagen gels, consisting of human dermal fibroblasts incorporated into a type I collagen lattice, was enhanced two-fold by exposure to peak E (P = 0.001). We conclude that a major constituent of contaminated batches of L-tryptophan, peak E, is a potent stimulus for fibroblast activation and collagen synthesis. This stimulatory action of peak E may provide a direct mechanism for the development of fibrosis in EMS.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belongia E. A., Hedberg C. W., Gleich G. J., White K. E., Mayeno A. N., Loegering D. A., Dunnette S. L., Pirie P. L., MacDonald K. L., Osterholm M. T. An investigation of the cause of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with tryptophan use. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):357–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blauvelt A., Falanga V. Idiopathic and L-tryptophan-associated eosinophilic fasciitis before and after L-tryptophan contamination. Arch Dermatol. 1991 Aug;127(8):1159–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boast S., Su M. W., Ramirez F., Sanchez M., Avvedimento E. V. Functional analysis of cis-acting DNA sequences controlling transcription of the human type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13351–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN G., BOHNER B. A confirmatory test for mephenesin-like action of a compound on mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):344–346. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Folkvord J. M., Hart C. E., Murray M. J., McPherson J. M. Platelet isoforms of platelet-derived growth factor stimulate fibroblasts to contract collagen matrices. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):1036–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI114227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauw D. J., Nashel D. J., Umhau A., Katz P. Tryptophan-associated eosinophilic connective-tissue disease. A new clinical entity? JAMA. 1990 Mar 16;263(11):1502–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofford L. J., Rader J. I., Dalakas M. C., Hill R. H., Jr, Page S. W., Needham L. L., Brady L. S., Heyes M. P., Wilder R. L., Gold P. W. L-tryptophan implicated in human eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome causes fasciitis and perimyositis in the Lewis rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1757–1763. doi: 10.1172/JCI114902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dans M. J., Isseroff R. Inhibition of collagen lattice contraction by pentoxifylline and interferon-alpha, -beta, and -gamma. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jan;102(1):118–121. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falanga V., Katz M. H., Kirsner R., Alvarez A. F. The effects of endothelin-1 on human dermal fibroblast growth and synthetic activity. J Surg Res. 1992 Nov;53(5):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90099-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falanga V., Martin T. A., Takagi H., Kirsner R. S., Helfman T., Pardes J., Ochoa M. S. Low oxygen tension increases mRNA levels of alpha 1 (I) procollagen in human dermal fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Nov;157(2):408–412. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falanga V., Qian S. W., Danielpour D., Katz M. H., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Hypoxia upregulates the synthesis of TGF-beta 1 by human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):634–637. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12483126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzman P. A., Blevins W. L., Mayer J., Greenfield B., Ting M., Gleich G. J. Association of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. H., Jr, Caudill S. P., Philen R. M., Bailey S. L., Flanders W. D., Driskell W. J., Kamb M. L., Needham L. L., Sampson E. J. Contaminants in L-tryptophan associated with eosinophilia myalgia syndrome. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1993 Jul;25(1):134–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00230724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illa I., Dinsmore S., Dalakas M. C. Immune-mediated mechanisms and immune activation of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome induced by L-tryptophan. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jul;24(7):702–709. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Varga J., Olsen A., Li L., Diaz A., Herhal J., Koch J. Functional analysis of human alpha 1(I) procollagen gene promoter. Differential activity in collagen-producing and -nonproducing cells and response to transforming growth factor beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12684–12691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love L. A., Rader J. I., Crofford L. J., Raybourne R. B., Principato M. A., Page S. W., Trucksess M. W., Smith M. J., Dugan E. M., Turner M. L. Pathological and immunological effects of ingesting L-tryptophan and 1,1'-ethylidenebis (L-tryptophan) in Lewis rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):804–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI116300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeno A. N., Lin F., Foote C. S., Loegering D. A., Ames M. M., Hedberg C. W., Gleich G. J. Characterization of "peak E," a novel amino acid associated with eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1707–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.2270484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Heyes M. P., Maize J. C., Quearry B., Vionnet-Fuasset M., Sternberg E. M. Scleroderma, fasciitis, and eosinophilia associated with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):874–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Ludwicka A., Hampton M., Ohba T., Bingel S. A., Smith T., Harley R. A., Maize J., Heyes M. P. A murine model of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome induced by 1,1'-ethylidenebis (L-tryptophan). J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1473–1480. doi: 10.1172/JCI117125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Jimenez S. A. Chemical exposure-induced cutaneous fibrosis. Lessons from 'experiments of nature'. Arch Dermatol. 1994 Jan;130(1):97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Li L., Jimenez S. A. Increased type I collagen gene expression in L-tryptophan associated eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome skin fibroblasts. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1303–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Li L., Mauviel A., Jeffrey J., Jimenez S. A. L-Tryptophan in supraphysiologic concentrations stimulates collagenase gene expression in human skin fibroblasts. Lab Invest. 1994 Feb;70(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster D. F., Harvey W. A quantitative assay for collagen synthesis in microwell fibroblast cultures. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K. A., Miyasaka N., Inuo G., Saito I., Kolb J. P., Fujita K., Kashiwazaki S. 1,1'-Ethylidenebis(tryptophan) (Peak E) induces functional activation of human eosinophils and interleukin 5 production from T lymphocytes: association of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with a L-tryptophan contaminant. J Clin Immunol. 1994 Jan;14(1):50–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01541175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]