Abstract
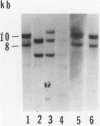
Inbred CE/J mice have been identified as extremely resistant to azocasein-induced amyloidosis relative to five commonly used inbred strains, A/J, CBA/J, C57BL/6J, C3H/HeN, and SJL/J. The enhanced amyloid resistance in CE/J mice seems to derive from the novel structure of the SAA gene family in CE/J mice, as determined by Southern blot hybridization analysis of SAA gene structure and isoelectric focusing analysis of acute phase SAA proteins in the six inbred strains. In CE/J mice, a single, novel SAA isoform of pI 6.15 is present, whereas in the other strains the amyloidogenic SAA2 isoform (pI 6.3) is codominantly expressed with SAA1 (pI 6.45). Two other inbred strains, PERU and IS/CAM, share common SAA specific HindIII DNA fragments with CE/J mice. Wild-derived Mus musculus mice differ from all of the inbred strains studied, both in SAA gene structure and in the pattern of SAA isoform production; two isoforms, one pI 6.15 and the other pI 6.3 (corresponding to SAA2), were codominantly expressed. Only the pI 6.15 isoform, not SAA1 and 2, was produced by CE/J mice in response to lipopolysaccharide, casein, silver nitrate, interleukin-1, or tumor necrosis factor; tumor necrosis factor was a weaker stimulus than interleukin-1 for the pI 6.15 isoform as it is for SAA1 and 2 production in the other inbred strains. This study provides a new line of evidence supporting the role of precursor structure as a determining factor in murine amyloid A amyloidosis and provides a valuable model for studies of amyloidogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrad M. A., Kisilevsky R., Willmer J., Chen S. J., Skinner M. Further characterization of amyloid-enhancing factor. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach C. M., De Beer M. C., Sipe J. D., Loose L. D., De Beer F. C. Human serum amyloid A protein. Complete amino acid sequence of a new variant. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 1;282(Pt 2):615–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2820615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Hoffman J. S., Eriksen N., Parmelee D. C., Walsh K. A. SAA, an apoprotein of HDL: its structure and function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:183–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Page D. L. Amyloid, amyloidosis, and amyloidogenesis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;15:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godenir N. L., Jeenah M. S., Coetzee G. A., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Strachan A. F., De Beer F. C. Standardisation of the quantitation of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janigan D. T., Druet R. L. Experimental amyloidosis. Role of antigenicity and rapid induction. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jun;48(6):1013–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R. From arthritis to Alzheimer's disease: current concepts on the pathogenesis of amyloidosis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;65(9):1805–1815. doi: 10.1139/y87-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., Benson M. D. DNA sequence evidence for polymorphic forms of human serum amyloid A (SAA). Biochem Genet. 1986 Dec;24(11-12):795–803. doi: 10.1007/BF00554519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Potter D. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Structure of the murine serum amyloid A gene family. Gene conversion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8442–8452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek R. L., Eriksen N., Benditt E. P. Murine serum amyloid A3 is a high density apolipoprotein and is secreted by macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7949–7952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Glenner G. G. Social interaction and wounding in the genesis of "spontaneous" murine amyloidosis. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jun;67(3):555–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokita H., Shirahama T., Cohen A. S., Sipe J. D. Serum amyloid A gene expression and AA amyloid formation in A/J and SJL/J mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1989 Jun;70(3):327–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Gonnerman W. A., Loose L. D., Knapschaefer G., Xie W. J., Franzblau C. Direct binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for serum amyloid A (SAA). J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Ignaczak T. F., Pollock P. S., Glenner G. G. Amyloid fibril protein AA: purification and properties of the antigenically related serum component as determined by solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1151–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Douches S., Neta R. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is a less potent inducer of serum amyloid A synthesis than interleukin 1. Lymphokine Res. 1987 Spring;6(2):93–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearman R. S., Lowell C. A., Peltzman C. G., Morrow J. F. The sequence and structure of a new serum amyloid A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):797–809. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan A. F., Brandt W. F., Woo P., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A., de Beer M. C., Shephard E. G., de Beer F. C. Human serum amyloid A protein. The assignment of the six major isoforms to three published gene sequences and evidence for two genetic loci. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18368–18373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan A. F., de Beer F. C., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A. Identification of three isoform patterns of human serum amyloid A protein. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):203–207. doi: 10.1042/bj2500203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Rowe L. Genes for serum amyloid A proteins map to Chromosome 7 in the mouse. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):491–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00341452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Skinner M., Bruns G. A., Costello W., Edge M. D., Cohen A. S., Sipe J. D. Cloning of human prealbumin complementary DNA. Localization of the gene to chromosome 18 and detection of a variant prealbumin allele in a family with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Dec;2(6):411–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgethan J. R., Cathcart E. S. Amyloid resistance in A/J mice is determined by a single gene. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):453–454. doi: 10.1038/278453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgethan J. R., Cathcart E. S. Amyloid resistance in A/J mice. Studies with a transfer model. Lab Invest. 1980 Jun;42(6):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Migita S. Complete primary structures of two major murine serum amyloid A proteins deduced from cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2915–2919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Shiroo M., Migita S. Diverse gene expression for isotypes of murine serum amyloid A protein during acute phase reaction. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):227–229. doi: 10.1126/science.3456645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer M. C., Beach C. M., Shedlofsky S. I., de Beer F. C. Identification of a novel serum amyloid A protein in BALB/c mice. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):45–49. doi: 10.1042/bj2800045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer M. C., de Beer F. C., Beach C. M., Carreras I., Sipe J. D. Mouse serum amyloid A protein. Complete amino acid sequence and mRNA analysis of a new isoform. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2830673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]