Figure 1.
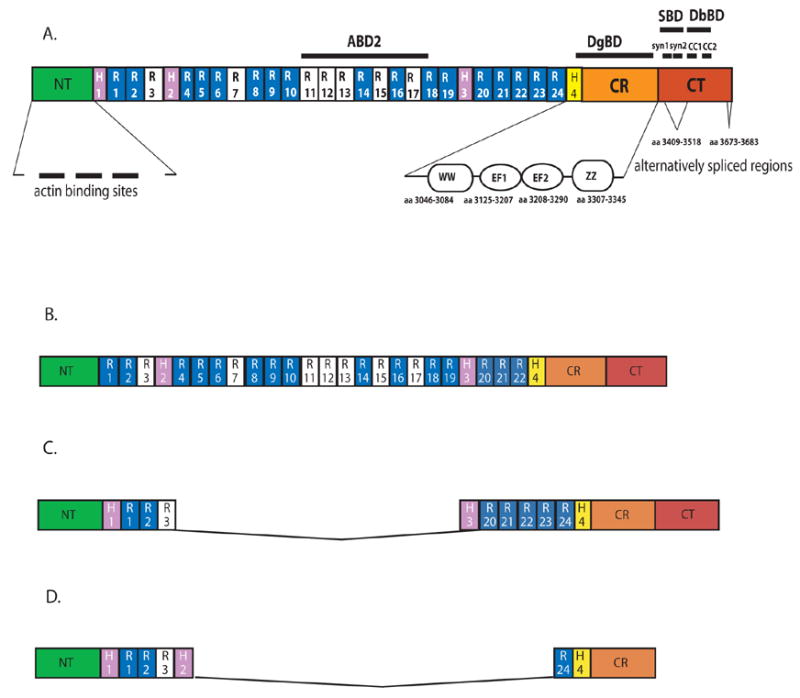
Structural domains of the human dystrophin protein referred to in the text (scale is approximate). A. Dystrophin (427 KDa); B. Utrophin (395 KDa); C. Mini-dystrophin ΔH2-R19Δ (227 KDa); D. Micro-dystrophin ΔR4-R23 (132 KDa).
ABD: actin-binding domains; H: hinge regions; R: spectrin-like repeats; CR: cysteine-rich domain; CT: C-terminal domain; CH: calponin homology motifs; WW: WW domain; EF: EF-hand motifs; ZZ: ZZ domain; DgBD: dystroglycan-binding domain; SBD: syntrophin-binding domain; DbBD: dystrobrevin-binding domain; syn: location of the syntrophin contact sites (syn1 spans amino acids 3427–3461; syn2 spans amino acids 3462–3483); CC: coiled coil motifs (CC1 spans amino acids 3506–3593; CC2 spans amino acids 3558–3593 as determined from the primary cDNA sequence). Hinge 4 spans amino acids 3041–3112.23 Basic repeats are shown in white, the others in blue. The location of the alternatively spliced exons is from Feener, CA Nature 1999.
