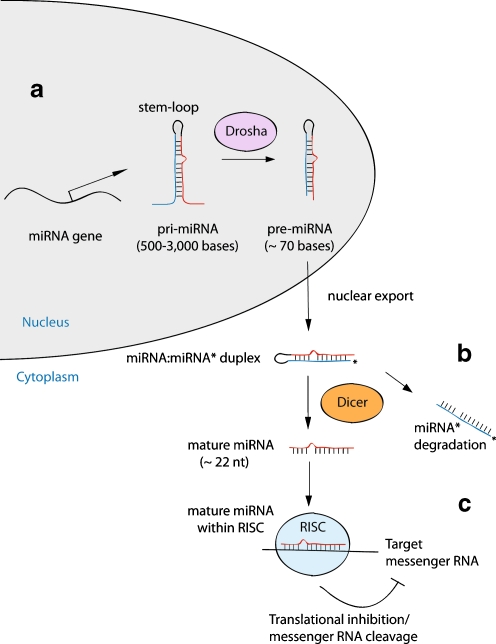
Fig. 1.
The biogenesis and function of miRNAs. a Primary miRNAs (pri-miRNA) are transcribed from longer encoding DNA sequences (miRNA genes). The pri-miRNA contains one or more stem-loop structures of about 70 bases. In the nucleus, the ribonuclease enzyme Drosha excises the stem-loop structure to form the precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA). b After export into the cytoplasm, the pre-miRNA is cleaved by the ribonuclease Dicer to generate a short RNA duplex (miRNA:miRNA*). c The mature single-stranded miRNA is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), while the complementary strand (miRNA*) is usually rapidly degraded. The miRNA incorporated into the silencing complex can bind to the target messenger RNA by base pairing, causing inhibition of protein translation and/or degradation of the target messenger RNA