Abstract
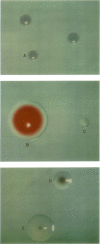
Pseudomonas putida PpF1 degraded toluene via a dihydrodiol pathway to tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates. The initial reaction was catalyzed by a multicomponent enzyme, toluene dioxygenase, which oxidized toluene to (+)-cis-1(S),2(R)-dihydroxy-3-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene (cis-toluene dihydrodiol). The enzyme consisted of three protein components: NADH-ferredoxintol oxidoreductase (reductasetol), ferredoxintol, and a terminal oxygenase which is an iron-sulfur protein (ISPtol). Mutants blocked in each of these components were isolated after mutagenesis with nitrosoguanidine. Mutants occurred as colony morphology variants when grown in the presence of toluene on indicator plates containing agar, mineral salts, a growth-supporting nutrient (arginine), 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC), and Nitro Blue Tetrazolium (NBT). Under these conditions, wild-type colonies appeared large and red as a result of TTC reduction. Colonies of reductasetol mutants were white or white with a light blue center, ferredoxintol strains were light blue with a dark blue center, and strains that lacked ISPtol gave dark blue colonies. Blue color differences in the mutant colonies were due to variations in the extent of NBT reduction. Strains lacking all three components appeared white. Toluene dioxygenase mutants were characterized by assaying toluene dioxygenase activity in crude cell extracts which were complemented with purified preparations of each protein component. Between 40 and 60% of the putative mutants selected from the NBT-TTC indicator plates were unable to grow with toluene as the sole source of carbon and energy. This method should prove extremely useful in isolating mutants in other multicomponent oxygenase enzyme systems.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axcell B. C., Geary P. J. Purification and some properties of a soluble benzene-oxidizing system from a strain of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):173–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1460173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Wigmore G. J. Metabolism of phenol and cresols by mutants of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1112–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1112-1120.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Savageau M. A. Generalized indicator plate for genetic, metabolic, and taxonomic studies with microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):434–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.434-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUS D., WALKER N. THE DECOMPOSITION OF TOLUENE BY SOIL BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jul;36:107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardini G., Jurtshuk P. The enzymatic hydroxylation of n-octane by Corynebacterium sp. strain 7E1C. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2789–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carhart G., Hegeman G. Improved method of selection for mutants of Pseudomonas putida. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1046–1047. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1046-1047.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Dalton H. Characterization of the second prosthetic group of the flavoenzyme NADH-acceptor reductase (component C) of the methane mono-oxygenase from Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath). Biochem J. 1979 Mar 1;177(3):903–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1770903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Dalton H. Resolution of the methane mono-oxygenase of Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath) into three components. Purification and properties of component C, a flavoprotein. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):461–468. doi: 10.1042/bj1710461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., CHAPMAN P. J., GIBSON D. T., WOOD J. M. DEGRADATION OF THE BENZENE NUCLEUS BY BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:775–778. doi: 10.1038/202775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Gibson D. T., Laborde A. L. Oxidation of naphthalene by a multicomponent enzyme system from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):948–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.948-954.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Gibson D. T. Naphthalene dioxygenase: purification and properties of a terminal oxygenase component. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.505-511.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa H., Yamaguchi M., Yamauchi T. Evidence for participation of NADH-dependent reductase in the reaction of benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase (benzoate hydroxylase). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:118–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary P. J., Dickson D. P. Mössbauer spectroscopic studies of the terminal dioxygenase protein of benzene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):199–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1950199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Hensley M., Yoshioka H., Mabry T. J. Formation of (+)-cis-2,3-dihydroxy-1-methylcyclohexa-4,6-diene from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymatic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2653–2662. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D. Genetic aspects of biodegradation by pseudomonads. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF01990357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri M., Ganguli B. N., Gunsalus I. C. A soluble cytochrome P-450 functional in methylene hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3543–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Ornston M. K., Chou G. Isolation of spontaneous mutant strains of Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90666-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Basu D., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. I. Electon carriers in fatty acid and hydrocarbon hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5162–5164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. E., Gibson D. T. Purification and properties of cis-toluene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1117–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1117-1124.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauber K., Fröhner C., Rosenberg G., Eberspächer J., Lingens F. Purification and properties of pyrazon dioxygenase from pyrazon-degrading bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):89–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Liu T. N., Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T. Toluene dioxygenase: purification of an iron-sulfur protein by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1131–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91998-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Liu T. N., Yeh W. K., Narro M., Gibson D. T. Purification and properties of NADH-ferredoxinTOL reductase. A component of toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2723–2730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai R. L., Gunsalus I. C., Dus K. Composition and structure of camphor hydroxylase components and homology between putidaredoxin and adrenodoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1300–1306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. Selective enrichment of Pseudomonas spp. defective in catabolism after exposure to halogenated substrates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):920–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.920-927.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: selective enrichment of defective mutants by using halogenated substrate analogs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):816–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.816-824.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Worsey M. J. Ubiquity of plasmids in coding for toluene and xylene metabolism in soil bacteria: evidence for the existence of new TOL plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):818–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.818-828.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Williams P. A. Metabolism of toluene and xylenes by Pseudomonas (putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for a new function of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.7-13.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Fujisawa H. Characterization of NADH-cytochrome c reductase, a component of benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase system from Pseudomonas arvilla c-1. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8848–8853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T., Liu T. N. Toluene dioxygenase: a multicomponent enzyme system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziffer H., Jerina D. M., Gibson D. T., Kobal V. M. Absolute stereochemistry of the (+)-cis-1,2-dihydroxy-3-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene produced from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 13;95(12):4048–4049. doi: 10.1021/ja00793a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]