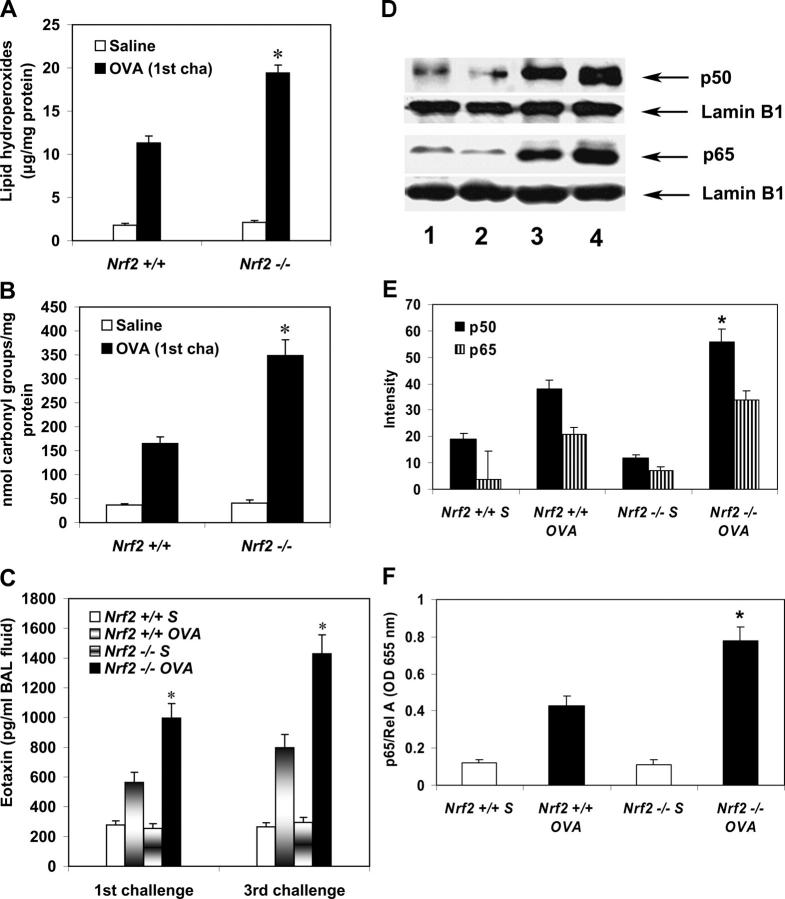
Figure 3.
Increased oxidative stress markers, eotaxin, and enhanced activation of NF-κB in the lungs of Nrf2 −/− OVA mice. Increased levels of lipid hydroperoxides (A) and protein carbonyls (B) in the lungs of OVA-challenged Nrf2 − / − mice. Values are mean ± SEM. *, Significantly higher than the Nrf2 + / + OVA mice (n = 6). (C) Eotaxin level in the BAL fluid. When compared with OVA-challenged Nrf2 + / + mice, the BAL eotaxin level was markedly higher in OVA-challenged (both first and third challenge) Nrf2 − / − mice (P ≤ 0.05; n = 6). (D–F) Activation of NF-κB in the lungs. Western blot was used to determine the activation of p50 and p65 subunits of NF-κB in the lungs (D). (lanes 1 and 2) Saline-challenged Nrf2 + / + and Nrf2 –/– mice, respectively; (lanes 3 and 4) OVA-challenged Nrf2 + / + and Nrf2 –/– mice, respectively. (E) Quantification of p50 and p65 subunits of NF-κB obtained in Western blots. Values are mean ± SEM of three experiments. (F) ELISA measurement of p65/Rel A subunit of NF-κB using Mercury TransFactor kit. *, P ≤ 0.05 versus OVA-challenged Nrf2 wild-type mice. Data are mean ± SEM of three experiments.