Figure 13. Hypocretin activates inward sodium current and depolarization.
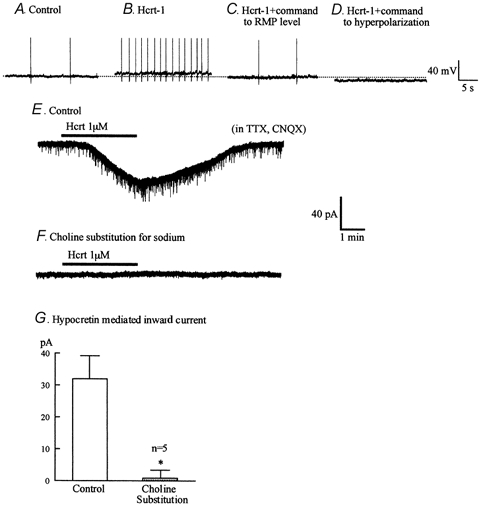
A-D, hypocretin-1 (1 μM) causes a depolarization and dramatic increase in spike frequency. When the membrane potential was returned to its control level (-60 mV) the number of spikes returned to a baseline frequency. When the cell was further hyperpolarized, spikes were stopped. E-F, hypocretin-1 (1 μM) evoked an inward current. When choline was substituted for sodium, hypocretin no longer evoked an inward current in the same cell that had previously responded to hypocretin. Holding potential −60 mV. G, bar graph showing the amplitude of inward current evoked by hypocretin in normal buffer and the same five cells after choline substitution. * Statistically significant difference (P < 0.05).
