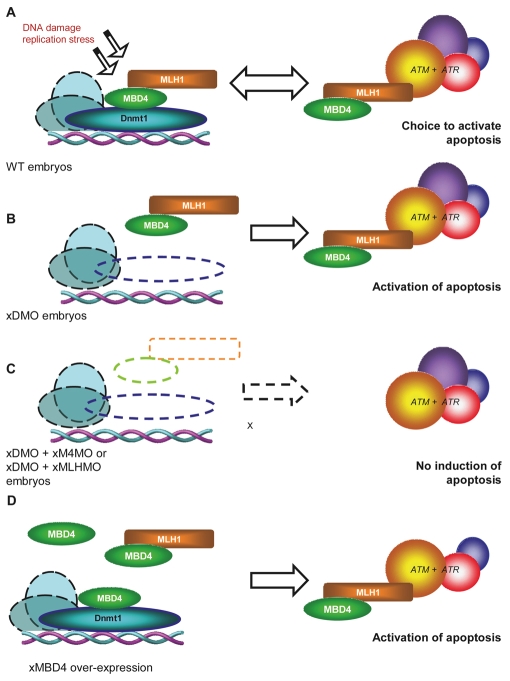
Fig. 8.
Model for the activation of xDNMT1-mediated apoptosis in Xenopus laevis embryos. (A) In normal embryos, we propose that a complex of xDNMT1, xMBD4 and xMLH1 is bound onto chromatin. This complex plays a role in responding to DNA damage or replication stress and is involved in the decision to repair the lesion or to activate an apoptotic response by releasing MBD4/MLH1 from xDNMT1; the MBD4/MLH1 complex signals probably via the DNA damage kinases ATM and ATR. (B) In xDMO morphants, a reduction of xDNMT1p levels results in abnormal activation (perhaps caused by release from a chromatin-bound complex) of the p53 apoptotic pathway via unbound MBD4/MLH1. (C) In xDMO/xM4MO or xDMO/xMLH1 double morphants, the p53 apoptotic pathway cannot be activated owing to the absence of the xMBD/xMLH1 complex. (D) Overexpression of MBD4 induces apoptosis via MLH1.