Abstract
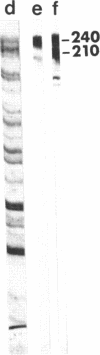
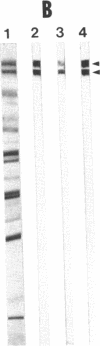
Desmoplakins (DPs) I and II (approximately equal to 240 and approximately equal to 210 kDa) are major components of the internal portion of the desmosomal cytoplasmic plaque. Desmosomes play a crucial role in cell-cell adhesion and serve as specific attachment sites for cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Although DP-I and -II are closely related molecules, their structure (i.e., amino acid or DNA sequence) has not been determined. In addition, it is not known whether these proteins are derived from one or more genes or whether they result from posttranscriptional or posttranslational events. This paper describes the isolation and characterization of eight DP cDNA clones from a bovine lambda gt11 expression library. Fusion proteins from six of these clones selected antibodies that reacted with DP-I and -II and two selected antibodies that reacted with DP-I alone. Antibodies made against fusion protein produced by the DP1A clone reacted specifically with DP-I and -II on immunoblots. When used for indirect immunofluorescence on bovine tongue cryostat sections and cultured mouse keratinocytes, these antibodies produced a typical desmosomal staining pattern. RNA blot analysis demonstrated hybridization of three DP-I/II cDNA probes with two messages of approximately equal to 7.5 and approximately equal to 9.5 kilobases in bovine tongue RNA. In contrast, a cDNA clone that affinity-purified antibodies reacting with DP-I only hybridized exclusively with the 9.5-kilobase band. Southern blots of genomic DNA digested with a panel of restriction enzymes were hybridized with one probe derived from a DP-I/II clone and with one from a DP-I clone. Both probes hybridized with single bands of the same size in each digested sample of DNA. Together, these data suggest that DP-I and DP-II are translated from two separate messages in bovine tongue and that these messages may be derived from a single gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou C. C., Davis R. C., Fuller M. L., Slovin J. P., Wong A., Wright J., Kania S., Shaked R., Gatti R. A., Salser W. A. Gamma-actin: unusual mRNA 3'-untranslated sequence conservation and amino acid substitutions that may be cancer related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2575–2579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Garrod D. R. Antibodies to epithelial desmosomes show wide tissue and species cross-reactivity. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):148–150. doi: 10.1038/302148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Kapprell H. P., Franke W. W. The complement of desmosomal plaque proteins in different cell types. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1442–1454. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Mattey D., Garrod D. Distribution of desmosomal components in the tissues of vertebrates, studied by fluorescent antibody staining. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:119–132. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenthal S., Parker V. P., Davidson N. Developmental variations in the splicing pattern of transcripts from the Drosophila gene encoding myosin alkali light chain result in different carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):449–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Moll R., Schiller D. L., Schmid E., Kartenbeck J., Mueller H. Desmoplakins of epithelial and myocardial desmosomes are immunologically and biochemically related. Differentiation. 1982;23(2):115–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod D. R. Desmosomes, cell adhesion molecules and the adhesive properties of cells in tissues. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:221–237. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigi-Leitner O., Geiger B. Antigenic interrelationship between the 40-kilodalton cytokeratin polypeptide and desmoplakins. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1986;6(6):628–639. doi: 10.1002/cm.970060611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Goldman R. D. The effects of taxol on cytoskeletal components in cultured fibroblasts and epithelial cells. Cell Motil. 1983;3(4):283–305. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Arnn J., Staehelin L. A., Goldman R. D. Human autoantibodies against desmosomes: possible causative factors in pemphigus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2781–2785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments and the initiation of desmosome assembly. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):506–517. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Vikstrom K. L., Goldman R. D. Evidence for heterogeneity in the 160/165 x 10(3) Mr glycoprotein components of desmosomes. J Cell Sci. 1987 Nov;88(Pt 4):513–520. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Yokoo K. M., Goldman R. D. Further analysis of pemphigus autoantibodies and their use in studies on the heterogeneity, structure, and function of desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1109–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapprell H. P., Cowin P., Franke W. W., Ponstingl H., Opferkuch H. J. Biochemical characterization of desmosomal proteins isolated from bovine muzzle epidermis: amino acid and carbohydrate composition. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;36(2):217–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Mattey D., Measures H., Hopkins C., Garrod D. Localisation of the protein and glycoprotein components of bovine nasal epithelial desmosomes by immunoelectron microscopy. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):885–889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunological characterization of desmoplakins I and II, the major polypeptides of the desmosomal plaque. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):647–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. A., Owens G. C., Prediger E. A., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Cell surface modulation of the neural cell adhesion molecule resulting from alternative mRNA splicing in a tissue-specific developmental sequence. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1431–1439. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Differential processing of RNA transcribed from the single-copy Drosophila myosin heavy chain gene produces four mRNAs that encode two polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A. Structure and function of intercellular junctions. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:191–283. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60940-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhrbier A., Garrod D. An investigation of the molecular components of desmosomes in epithelial cells of five vertebrates. J Cell Sci. 1986 Mar;81:223–242. doi: 10.1242/jcs.81.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Hollenberg S. M., Ong E. S., Harmon J. M., Brower S. T., Cidlowski J., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Identification of human glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA clones by epitope selection. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):740–742. doi: 10.1126/science.2581314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman A. E., Jones J. C., Steinert P. M., Goldman R. D. Isolation and characterization of keratin-like proteins from cultured cells with fibroblastic morphology. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1231–1237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. The chicken vimentin gene: aspects of organization and transcription during myogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:79–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]