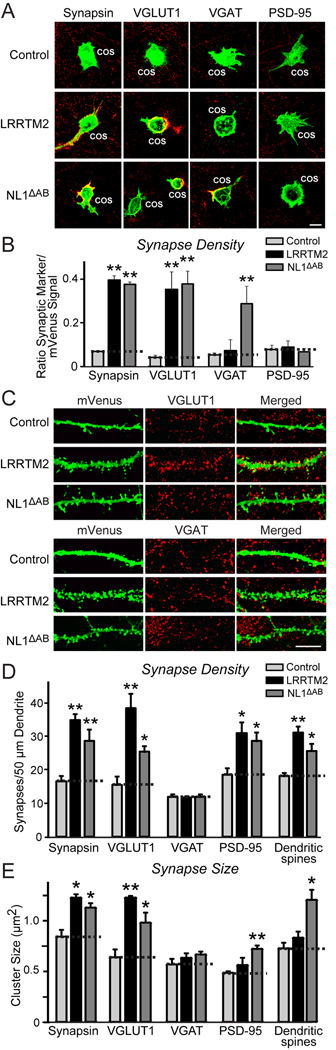
Figure 1. LRRTM2 Expression in COS cells and in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons Increases Excitatory Synapse Density.
A. LRRTM2 selectively promotes formation of excitatory synapses in the artificial synapse-formation assay. Hippocampal neurons were co-cultured for two days with COS cells expressing mVenus alone (control), an LRRTM2-mVenus fusion protein (LRRTM2), or an mVenus fusion protein of neuroligin-1 lacking inserts in splice sites A and B (NL1ΔAB). Panels show representative immunofluorescence images of the co-cultures stained with antibodies to mVenus (green; GFP) and to various pre- and postsynaptic markers (red; VGLUT1, vesicular glutamate transporter 1; VGAT, vesicular GABA transporter). Coincident green and red signals are shown in yellow (scale bar = 25 µm; applies to all images).
B. Quantitation of the artificial synapse formation activity of LRRTM2 and neuroligin-1. Experiments as described in A were quantified by measuring the ratio of the synaptic marker staining to mVenus fluorescence (for absolute red and green fluorescence values, see Figure S1).
C. Representative images of cultured hippocampal neurons that were transfected at DIV10 with mVenus alone (control), an LRRTM2 mVenus-fusion protein (LRRTM2), or an mVenus-fusion protein of neuroligin-1 lacking inserts in splice sites A and B (NL1ΔAB). Cultures were analyzed at DIV14 by double immunofluorescence with antibodies to mVenus and the synaptic markers described above for A (scale bar = 5 µm, applies to all images).
D. & E. Effect of LRRTM2 and neuroligin-1 on synapse density (D) and synaptic signal intensity (E), which were quantified with the indicated markers in neurons transfected with mVenus alone (control), the LRRTM2 mVenus-fusion protein (LRRTM2), or the neuroligin-1 mVenus-fusion protein (NL1ΔAB).
All data shown are means ± SEMs (n=3 independent culture experiments). Statistical significance was assessed by comparing the LRRTM2 and neuroligin-1 effects with the control using Student's t-test (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).