Figure 2.
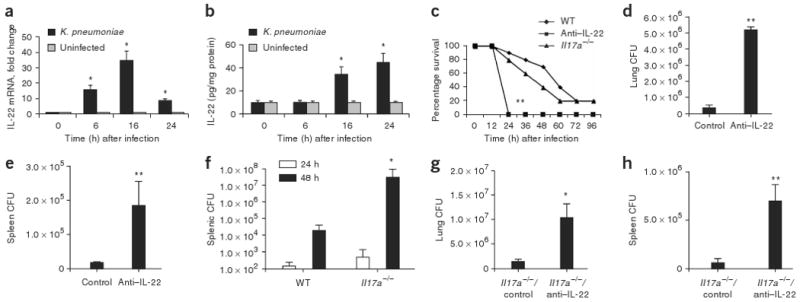
IL-22 expression is elevated in mice infected with K. pneumoniae, and neutralizing IL-22 leads to decreased bacterial clearance from lung and spleen. Mice were infected with K. pneumoniae and killed at the designated time points. (a) IL-22 mRNA was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Error bars represent means ± s.e.m. (b) IL-22 protein abundance was measured by ELISA and normalized per mg of protein. Error bars represent means ± s.e.m. (c) C57BL/6 and Il17a−/− mice were infected with K. pneumoniae and evaluated for survival. Mice given antibody to IL-22 (anti–IL-22) were moribund at 24 h compared to WT or Il17a−/− mice (n = 8–10, **P < 0.01 by log-rank test compared to Il17a−/− or WT mice). (d,e) K. pneumoniae burden in the lung (d) or spleen (e) 24 h after infection in control or anti–IL-22–treated mice. (f) K. pneumoniae burden in the spleen in WT or Il17a−/− mice at 24 and 48 h after infection. (g) K. pneumoniae burden in the lung 24 h after infection in control or anti–IL-22–treated Il17a−/− mice. n = 5–6 per group, *P < 0.05 compared with controls for panels a,b,f,g and **P < 0.01 compared with controls for d,e. All values are mean ± s.e.m. (h) K. pneumoniae burden in the spleen 24 h after infection in control or anti–IL-22–treated Il17a−/− mice (n = 5–6 per group and **P < 0.01 compared with controls).
