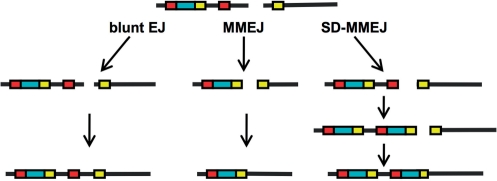
Figure 10.
Multiple mechanisms for alt-EJ. Alt-EJ can proceed by a variety of mechanisms: direct ligation of non-complementary blunt ends (left), annealing at pre-existing microhomologies (center) or synthesis of de novo microhomologies via SD-MMEJ (right). Deletions during direct ligation of blunt ends are not influenced by repeated sequences. MMEJ at pre-existing microhomologies (yellow) involves deletion of one of the two repeated motifs as well as all sequence intervening between the repeated motifs. SD-MMEJ synthesizes de novo microhomologies via priming at a repeat situated entirely to one side of the DSB (red). Any sequence intervening between the primer and the template for the new microhomology (blue) is copied and inserted at the break site. Identically colored boxes represent direct repeats. See also Supplementary Figures S5 and S6.