Abstract
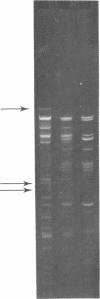
Transfer of octopine Ti plasmids to strains already carrying an octopine Ti plasmid was found to occur at the same (high) frequency as transfer to Ti plasmid lacking recipients, showing that resident Ti plasmids do not exhibit entry exclusion towards incoming Ti plasmids. The resident octopine Ti plasmid was lost by the recipient after the entrance of the incoming Ti plasmid, which is indicative of the incompatibility between the Ti plasmids. Octopine Ti plasmids were found to become established only infrequently in recipients with a nopaline Ti plasmid and, vice versa, nopaline Ti plasmids were only rarely established in recipients with an octopine Ti plasmid. Rare clones in which the incoming octopine (nopaline) Ti plasmid had been established despite the presence of a nopaline (octopine) Ti plasmid appeared to harbor cointegrates consisting of the entire incoming Ti plasmid and the entire resident Ti plasmid. The integration event invariably had occurred in a region of the plasmids that is highly conserved in evolution and that is essential for oncogenicity. These results show that octopine and nopaline Ti plasmids cannot be maintained as separate replicons by one and the same cell. Therefore, be definition, these plasmids belong to the same incompatibility group, which has been names inc Rh-1. Agrobacterial non-Ti octopine and nopaline plasmids were found to belong to another incompatibility group. The tumorigenic properties of strains harboring two different Ti plasmids, in a cointegrate structure, were indicative of the virulence genes of both of them being expressed. The agrobacterial non-Ti octopine and nopaline plasmids did not influence the virulence properties encoded by the Ti plasmid.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedbrook J. R., Lehrach H., Ausubel F. M. Directive segregation in the basis of colE1 plasmid incompatibility. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):447–452. doi: 10.1038/281447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomhoff G., Klapwijk P. M., Kester H. C., Schilperoort R. A., Hernalsteens J. P., Schell J. Octopine and nopaline synthesis and breakdown genetically controlled by a plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):177–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00269591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Friello D. A., Bopp L. H. Transposition of plasmid DNA segments specifying hydrocarbon degradation and their expression in various microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3109–3112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Montoya A. L., Merlo D. J., Drummond M. H., Nutter R., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Restriction endonuclease mapping of a plasmid that confers oncogenicity upon Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain B6-806. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):254–269. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., De Wilde M., De Vos G., De Vos R., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Molecular cloning of overlapping segments of the nopaline Ti-plasmid pTiC58 as a means to restriction endonuclease mapping. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):193–211. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Chilton M. D. Tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmids of Agrobacterium share extensive regions of DNA homology. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1178–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1178-1183.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of R factor compatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):387–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.387-398.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Achtman M. Operon structure of DNA transfer cistrons on the F sex factor. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):652–656. doi: 10.1038/257652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsters M., Silva B., Van Vliet F., Genetello C., De Block M., Dhaese P., Depicker A., Inzé D., Engler G., Villarroel R. The functional organization of the nopaline A. tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):212–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., den Dulk-Ras H., Schilperoort R. A. Molecular mechanism of Ti plasmid mobilization by R plasmids: isolation of Ti plasmids with transposon-insertions in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1980 Jul;4(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Incompatibility-deficient derivatives of a small staphylococcal plasmid. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Matsubara K. Random replication and random assortment model for plasmid incompatibility in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Rogers J. E., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Transposition of Pseudomonas toluene-degrading genes and expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):179–180. doi: 10.1038/274179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapwijk P. M., Scheulderman T., Schilperoort R. A. Coordinated regulation of octopine degradation and conjugative transfer of Ti plasmids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: evidence for a common regulatory gene and separate operons. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):775–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.775-785.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapwijk P. M., Schilperoort R. A. Negative control of octopine degradation and transfer genes of octopine Ti plasmids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):424–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.424-431.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koekman B. P., Ooms G., Klapwijk P. M., Schilperoort R. A. Genetic map of an octopine TI-plasmid. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Cohen S. N. Genetic analysis of the inter-relationship between plasmid replication and incompatibility. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 13;174(2):135–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00268351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin S., Nordström K. Control of plasmid R1 replication: functions involved in replication, copy number control, incompatibility, and switch-off of replication. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.111-120.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya A. L., Chilton M. D., Gordon M. P., Sciaky D., Nester E. W. Octopine and nopaline metabolism in Agrobacterium tumefaciens and crown gall tumor cells: role of plasmid genes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.101-107.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya A. L., Moore L. W., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Multiple genes coding for octopine-degrading enzymes in Agrobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.909-915.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Hoppensteadt F. C. On plasmid incompatibility. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten L. A., Schilperoort R. A. A rapid micro scale method for the detection of lysopine and nopaline dehydrogenase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 8;527(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciaky D., Montoya A. L., Chilton M. D. Fingerprints of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):238–253. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard H. M., Gelfand D. H., Polisky B. Analysis of a recessive plasmid copy number mutant: evidence for negative control of Col E1 replication. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terawaki Y., Kobayashi Y. Further characterization of the R plasmid Rts1 and its mutant pTW2: replication and incompatibility of the plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):300–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.300-306.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Nordström K. Plasmid incompatibility and control of replication: copy mutants of the R-factor R1 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):641–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.641-649.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]