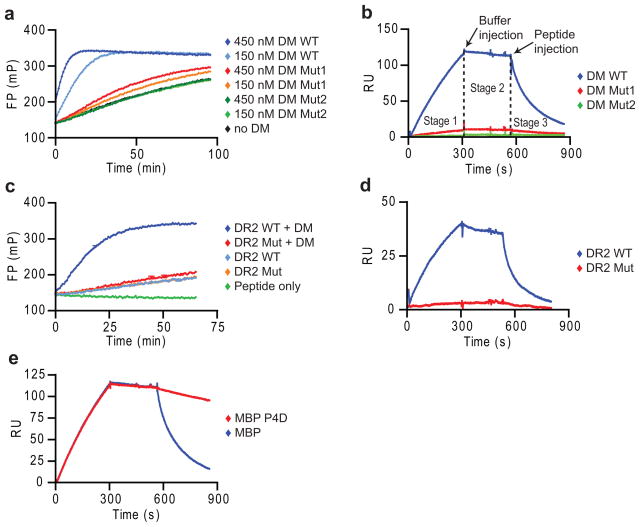
Figure 1. Peptide disrupts long-lived complex between empty DR and DM.
(a,b) Specificity of SPR assay. (a) Activity of DM WT, Mut1 (DMα R98A) and Mut2 (DMα R98A/R194A) in accelerating binding of Alexa-488 labeled MBP85-99 peptide (30 nM) to DR2 (150 nM), measured by fluorescence polarization (FP). (b) Binding of DR2-CLIP complexes to DM WT and mutants by SPR. DR2-CLIP (2 μM) was run over DM WT and mutant surfaces (5 min, pH 5.35, 25 μl/min, 30°C) (stage 1), followed by buffer (stage 2) and 1 μM MBP85-99 (stage 3). Readings from streptavidin flow cell were subtracted from DM WT and mutant flow cells. (c,d) DR2 mutant without DM interaction. (c) DM-accelerated binding (+/− 25 nM DM) of labeled MBP85-99 to DR2 WT and DRα S53D mutant (150 nM) was measured as in (a). (d) DM binding of DR2 WT and mutant. WT or mutant DR2-CLIP (1 μM) were injected (5 min), followed by buffer and 10 μM CLIP87-101. (e) Dissociation of DM-DR2 complex by high-affinity peptide. DR2-CLIP complexes (2 μM) were injected (5 min), followed by buffer and MBP85-99 or MBP P4D analog (1 μM). Data are representative of two (a, c, d) or more than three (b, e) independent experiments.