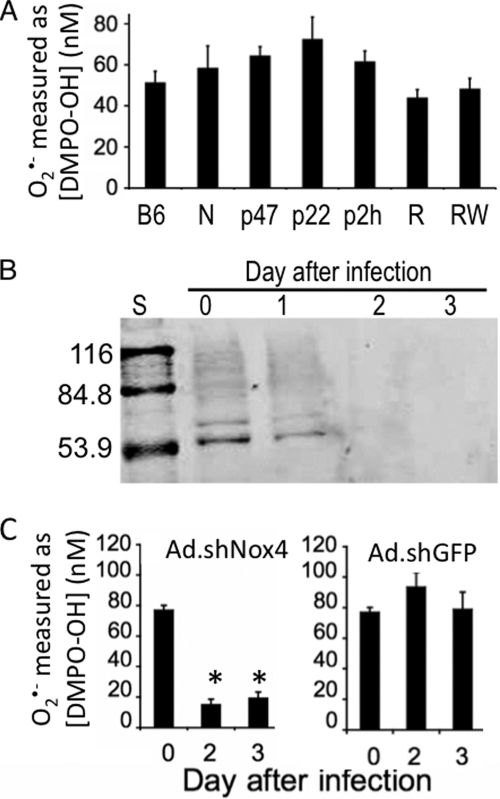
FIGURE 2.
NOX4 is the predominant source of NADPH-dependent O2⨪ production in isolated hepatic nuclei. A, nuclei were isolated from livers of several knock-out or mutant mice and tested for level of O2⨪ production by EPR. Specific genotypes of mice are labeled as follows: wild-type C57BL6 (B6), NOX1,2 double knock-out (N), p47 homozygous mutant (p47), p22phox homozygous mutant (p22), p22phox heterozygous mutant (p2h), Alb-Cre Rac1flx/flx/Rac2-KO double knock-out (R), and Rac1flx/flx/Rac2-WT (RW). The nuclei from each of these genotypes were assayed for O2⨪ production levels in the presence of 0.1 mm NADPH by EPR spin trapping using DMPO after 5 min of incubation at 22 °C. All of the results demonstrate no statistically significant difference (i.e. p > 0.05) compared with the controls B6, p2h, or RW, as determined by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's multiple comparison tests. B, Ad.shNOX4 hepatic infection efficiently reduces nuclear NOX4 protein. The livers of B6SJLF1 mice were infected with Ad.shNOX4 to knock down NOX4. The nuclei were isolated, resolved by SDS-PAGE (10 μg protein/lane), and Western blotted for NOX4 protein using a rabbit anti-NOX4 antibody. S, protein standard ladder with molecular masses in kDa listed on the left. Days post-infection with Ad.shNOX4 are indicated above the blot. The blot is representative of two independent time course experiments. C, shRNA targeted to mouse NOX4 decreases nuclear ROS production. The livers of B6SJLF1 mice were infected with Ad.shNOX4 (left panel) to knock down NOX4 or with Ad.shGFP (right panel) as a control virus. Daily after infection, a subset of the mice was sacrificed, and the liver nuclei were isolated and assayed for O2⨪ production levels in the presence of 0.1 mm NADPH by EPR. EPR spectra were quantitated as in Fig. 1. The error bars represent average [DMPO-OH] ± S.E., n = 3–6 animals for each experimental point. To determine statistical significance, ANOVA and Bonferroni's multiple comparison test were performed. *, statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) compared with the day 0 control.