Abstract
Expansion of (AGC)n repeats has been associated with genetic disorders called triplet-repeat diseases such as Huntington's disease (HD), myotonic muscular dystrophy (DM) and Kennedy's disease. To gain insight into the abnormal behavior of these repeats, we studied their structural properties in supercoiled DNA. Chemical probing revealed that, under physiological salt and pH conditions, Zn2+ or Co2+ ions induce (AGC)n repeats to adopt a novel non-B DNA structure in which all cytosine but none of adenine residues in either strand become unpaired. The minimum size of (AGC)n repeat that could form this structure independently of neighboring sequences is a single unit of double-stranded trinucleotide, 5'AGC3'/5'GCT3'. Other trinucleotide units of the same nucleotide composition, 5'CAG3'/5'CTG3' or 5'GCA3'/5'TGC3', do not form non-B DNA structures. This unusual DNA structural properly adopted by a single 5'AGC3'/5'GCT3' trinucleotide may contribute to expansion of (AGC)n sequences in triplet-repeat diseases.
Full text
PDF

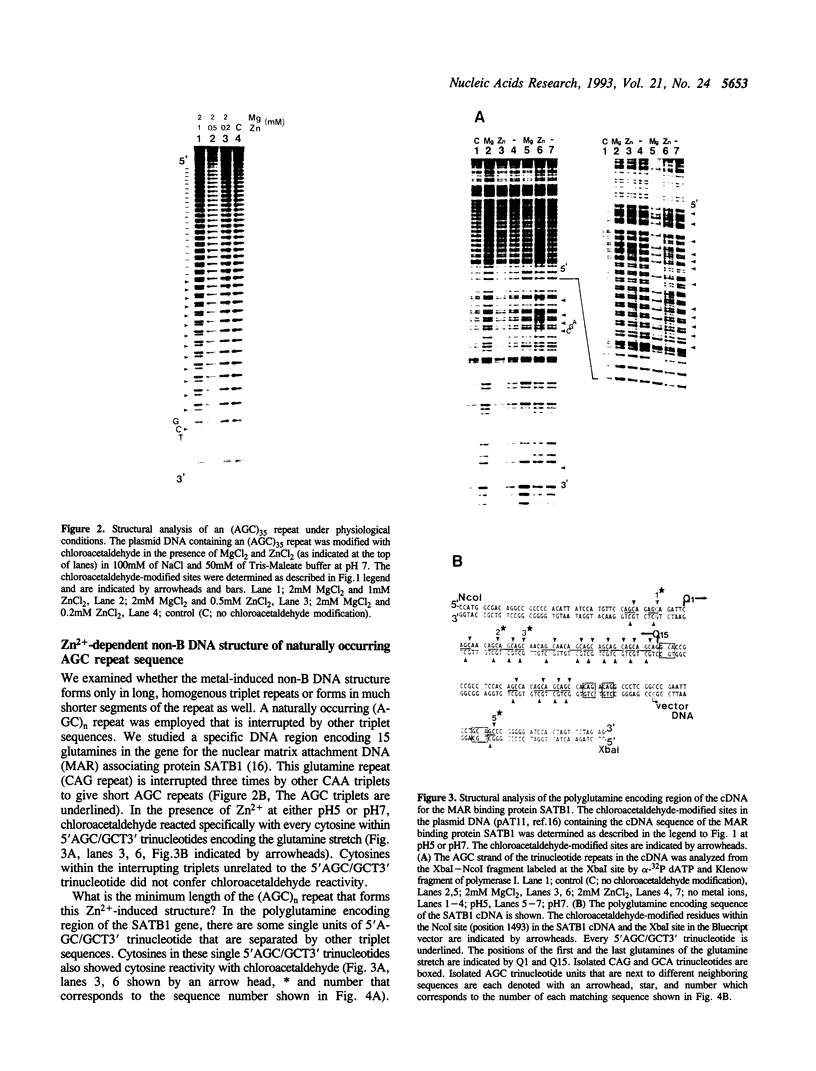


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslanidis C., Jansen G., Amemiya C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Chen C., Alleman J., Wormskamp N. G., Vooijs M. Cloning of the essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):548–551. doi: 10.1038/355548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Kohwi Y., Dickinson L., Joh T., Klehr D., Mielke C., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Biological significance of unwinding capability of nuclear matrix-associating DNAs. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.1553545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., McCurrach M. E., Harley H. G., Buckler A. J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V. P., Thirion J. P., Hudson T. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton J., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Jones C., Van Tongeren T., Aslanidis C., de Jong P., Jansen G., Anvret M., Riley B. Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):547–548. doi: 10.1038/355547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson L. A., Joh T., Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. A tissue-specific MAR/SAR DNA-binding protein with unusual binding site recognition. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):631–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90432-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich A., Kioschis P., Monaco A. P., Gross B., Korn B., Williams S. V., Sheer D., Heitz D., Oberle I., Toniolo D. Molecular cloning and analysis of the fragile X region in man. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2567–2572. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Reardon W., Buckler A. J., Harper P. S., Housman D. E., Shaw D. J. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):545–546. doi: 10.1038/355545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Kohwi Y. Torsional stress stabilizes extended base unpairing in suppressor sites flanking immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9551–9560. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y. Cationic metal-specific structures adopted by the poly(dG) region and the direct repeats in the chicken adult beta A globin gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4493–4502. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Altered gene expression correlates with DNA structure. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2547–2554. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Malkhosyan S. R., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Intramolecular dG.dG.dC triplex detected in Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90242-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Panchenko Y. Transcription-dependent recombination induced by triple-helix formation. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1766–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Spada A. R., Wilson E. M., Lubahn D. B., Harding A. E., Fischbeck K. H. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):77–79. doi: 10.1038/352077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil G. Paranemic structures of DNA and their role in DNA unwinding. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(5-6):475–559. doi: 10.3109/10409239109086791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






