Figure 6.
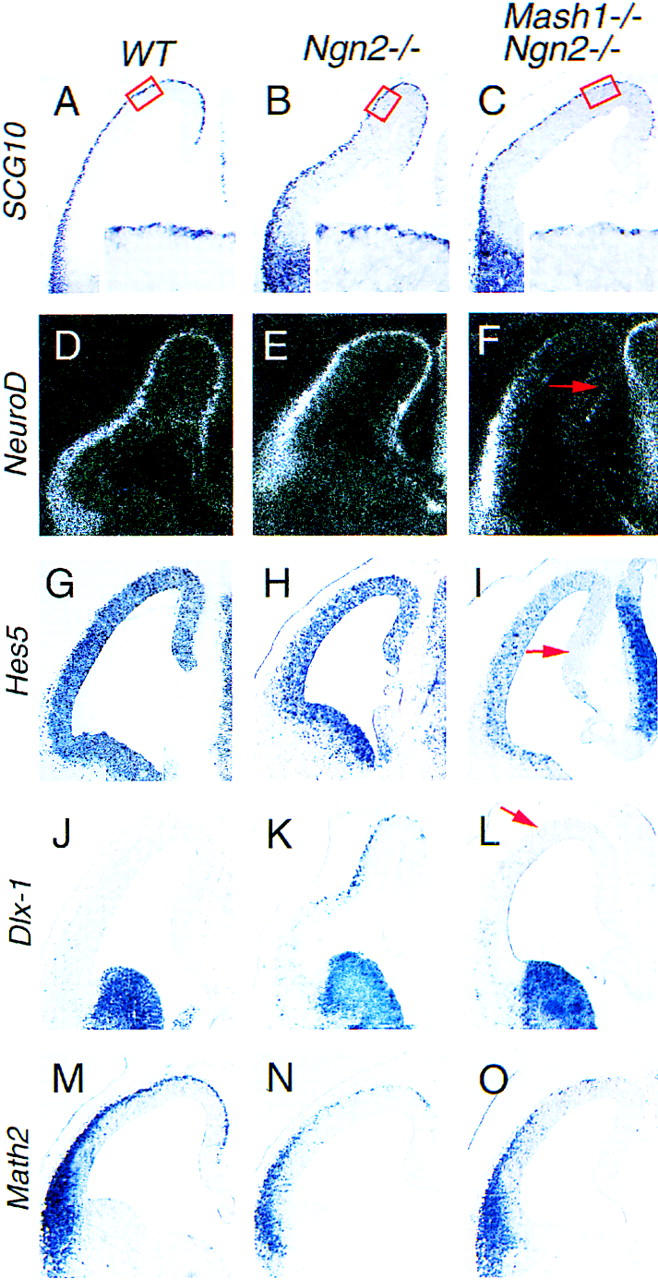
Up-regulation of Mash1 is required for the mis-specification of cortical neurons in Ngn2 mutants. (A–C) Distribution of SCG10 transcripts in E12.5 wild-type, Ngn2 mutant, and Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant telencephalon. Neuronal loss is limited in the dorsal and medial PP of Ngn2 single mutants (B) and more severe in Ngn2;Mash1 double mutants (C). (D–F) Distribution of NeuroD transcripts in E12.5 wild-type, Ngn2 mutant, and Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant telencephalon. NeuroD expression is dramatically reduced in the dorsal and medial cortex of Ngn2;Mash1 double mutants (arrow, F) but is not affected in Ngn2 single mutants (E). (G–I) Distribution of Hes5 transcripts in E12.5 wild-type, Ngn2 mutant and Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant telencephalon. Hes5 expression is strongly down-regulated in the VZ of the dorsal and medial cortex of Ngn2;Mash1 double mutants (arrow, I), suggesting defects in Notch signaling in these progenitors. (J–L) Distribution of Dlx1 transcripts in E12.5 wild-type, Ngn2 mutant, and Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant telencephalon. Ectopic Dlx1+ neurons found in Ngn2 mutant cortex (K) are absent in Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant embryos (arrow in L). Up-regulation of Mash1 is thus involved in the generation of Dlx1+ cortical neurons in Ngn2 mutants. (M–O) Distribution of Math2 transcripts in E12.5 wild-type, Ngn2 mutant and, Ngn2;Mash1 double mutant telencephalon. The reduction in Math2 expression levels observed in the Ngn2 mutant cortex (N) is also found in Ngn2;Mash1 double mutants (O), thus confirming the overall reduction in number of medial and dorsal PP neurons in Ngn2;Mash1 double mutants.
