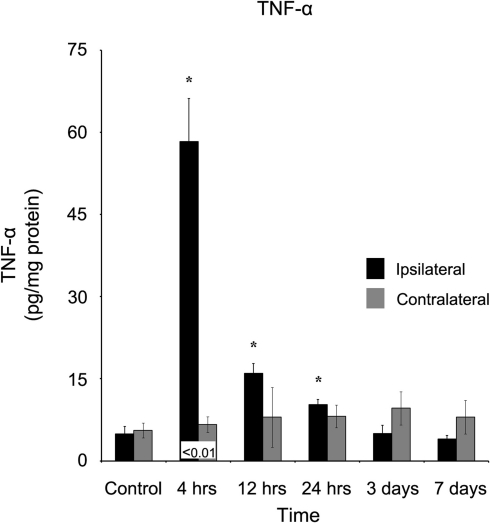
Figure 3.
TNF-α concentration increases in the ipsilateral cortex following a controlled cortical impact. Within four hours of a brain injury, TNF-α increases (p < 0.05) in the ipsilateral cortex in comparison to both control and contralateral tissue. TNF-α remained elevated for the first 24 hours following injury, before returning to control levels at three days, post-injury. In contrast, the contralateral cortex did not demonstrate an increase in TNF-α expression at any time point in comparison to control. All values are mean ± SEM, n = 5. *At each time point noted, ipsilateral differs from control tissue, p < 0.05. ±At each time point noted, contralateral differ from control tissue, p < 0.05. Differences between the ipsilateral and contralateral cortices are denoted by placing the appropriate p-value above the two bars.