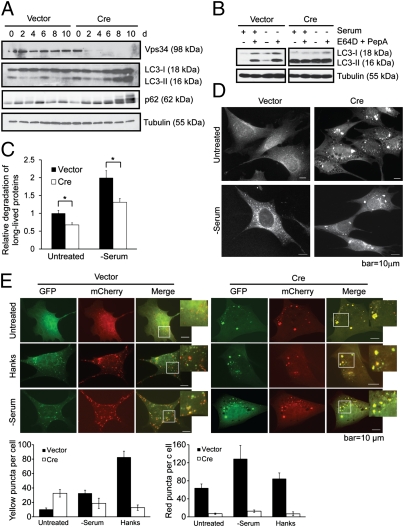
Fig. 2.
Autophagy flux is impaired in Vps34-null MEFs. (A) Vps34f/f MEFs were infected with control or Cre virus. Cell lysates were collected at indicated time points after infection and probed for Vps34, LC3, and p62. The fluctuation of the levels of LC3 and p62 in control cells may be due to the change of confluency during passaging. (B) Vps34f/f MEFs were infected with vector control or Cre. At 7 d after infection, cells were left untreated or serum deprived for 6 h, with or without the addition of lysosomal protease inhibitors E64D (10 μg/mL) and PepA (10 μg/mL). (C) MEFs were labeled with 14C-valine for 24 h and left untreated or cultured in serum-free medium for 6 h. Degradation of long-lived proteins was measured. Average of three independent experiments ± SEM is shown. *P < 0.05. (D) Vps34f/f MEFs infected with vector or Cre virus were cultured in serum-free medium for 6 h. Cells were stained for LC3 for immunofluorescence analysis. Note that although serum deprivation induces LC3 puncta in vector control cells, LC3 forms large-sized structures upon Cre infection, with no further increase upon serum starvation. (E) Vector and Cre-infected Vps34f/f MEFs were transfected with mCherry-GFP-LC3. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were starved in Hanks buffer or serum-free medium. Cells were observed under a deconvolution microscope. Representative images are shown. The average numbers of yellow or red puncta were obtained from three countings. Note although nutrient starvation induces both autophagosomes (yellow) and autolysosomes (red) in wild-type cells, both inductions are inhibited in Vps34-null cells.