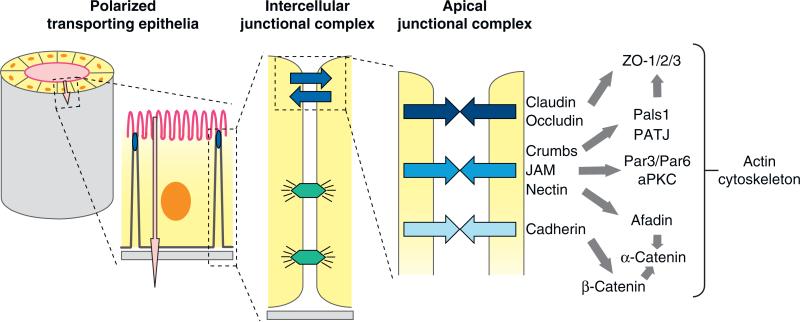
Figure 5.
Schematic representations of the epithelial synapse. Polarized transporting epithelia comprise a closed monolayer of cells that surround a fluid-filed space (lumen) and vectorially transport ions and solutes (pink arrow) between the luminal space and the serosa; the plasma membrane domains facing the lumen space (apical) and serosa (basal lateral) are structurally and functionally different. Intercellular junctional complexes regulate cell-cell adhesion and the paracellular pathway (blue arrows) as well as maintain the structural integrity of the epithelium (desmosomes, lower junctions). The apical junctional complex comprises different cell adhesion proteins and downstream protein networks, and it is located at the boundary between the apical and basal-lateral membranes. Abbreviations: aPKC, atypical protein kinase C; JAM, junction-associated molecule; Pals1, protein-associated with Lin-7; Par3/Par6, partition defective 3/6; PATJ, Pals1-associated tight junction protein.