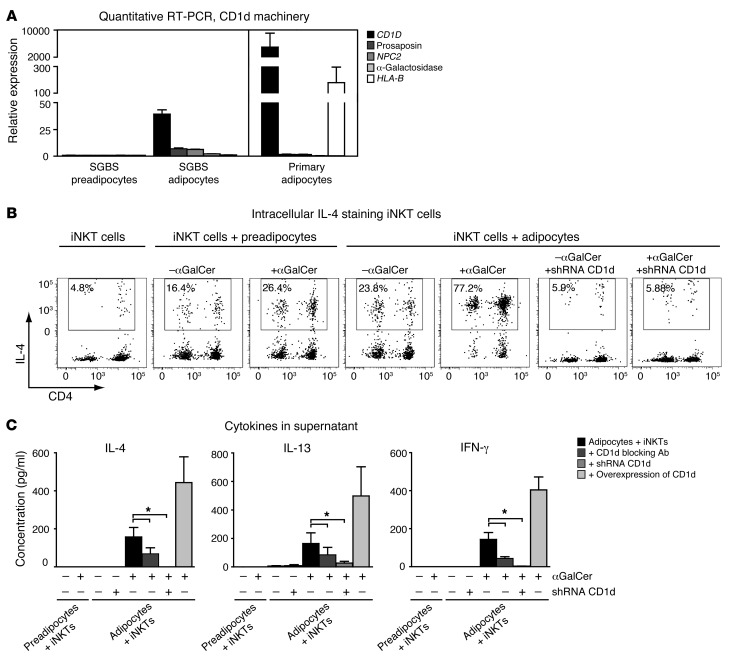
Figure 6. Adipocytes can modulate iNKT cell function in a CD1d-dependent manner.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCRs of CD1d and its lipid-loading machinery genes pro-saposin, NPC2, and α-galactosidase in human SGBS preadipocytes, mature adipocytes, and primary subcutaneous adipocytes isolated from 3 human subjects. HLA-B mRNA levels were included as a negative control. Fold changes were normalized for housekeeping genes (36B4 and β2 actin). (B) Intracellular IL-4 staining of iNKT cells cocultured with undifferentiated SGBS preadipocytes and mature adipocytes, with and without prior loading of the (pre)adipocytes with the CD1d-restricted iNKT cell ligand αGalCer. CD1d knockdown in the adipocytes depleted intracellular IL-4 staining in the cocultured iNKT cells. (C) IL-4, IL-13, and IFN-γ levels in the supernatants of iNKT cells cocultured with undifferentiated SGBS preadipocytes and mature adipocytes. Antibody blocking and CD1d knockdown of CD1d in mature adipocytes result in a significant decrease in IL-4, IL-13, and IFN-γ levels in the supernatants, while CD1d overexpression results in an increase. Data represent the mean results of 5 different iNKT cell lines cocultured with the (pre)adipocytes. *P < 0.05.