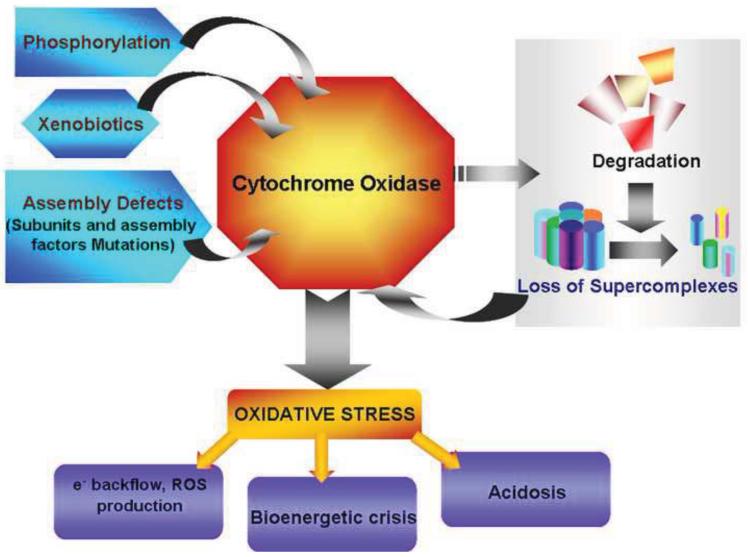
Figure 2.
Factors which cause dysfunction of Cytochrome C Oxidase. Multiple factors affect CcO function leading to mitochondrial stress and dysfunction. Genetic mutations of subunits and assembly factors are responsible for significant decrease in fully assembled complexes. Environmental changes such as hypoxia induce phosphorylation which either increase the activity or decrease activity by targeting the subunits for degradation. Many xenobiotics act by directly binding to active site heme and inhibit enzyme activity. Dysfunctional CcO contributes greatly to oxidative stress by increasing ROS production, ATP depletion and lactic acidosis.