Abstract
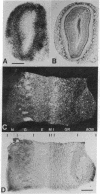
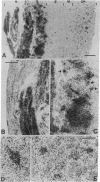
The spatial distribution of odor-induced neuronal activity in the olfactory bulb, the first relay station of the olfactory pathway, is believed to reflect important aspects of chemosensory coding. We report here the application of high-resolution 2-deoxyglucose autoradiography to the mapping of spatial patterns of metabolic activity at the level of single neurons in the olfactory bulb. It was found that glomeruli, which are synaptic complexes containing the first synaptic relay, tend to be uniformly active or inactive during odor exposure. Differential 2-deoxyglucose uptake was also observed in the somata of projection neurons (mitral cells) and interneurons (periglomerular and granule cells). This confirms and extends our previous studies in which odor-specific laminar and focal uptake patterns were revealed by the conventional x-ray film 2-deoxyglucose method due to Sokoloff and colleagues [Sokoloff, L., Reivich, M., Kennedy, C., DesRosiers, M. H., Patlak, C. S., Pettigrew, K. D., Sakurada, O. & Shinohara, M. (1977) J. Neurochem. 28, 897--916]. Based on results obtained by the two methods, it is suggested that the glomerulus as a whole serves as a functional unit of activity. The high-resolution results are interpreted in terms of the well-characterized synaptic organization of the olfactory bulb and also serve to illustrate the capability of the 2-deoxyglucose autoradiographic technique to map metabolic activity in single neurons of the vertebrate central nervous system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basinger S. F., Gordon W. C., Lam D. M. Differential labelling of retinal neurones by 3H-2-deoxyglucose. Nature. 1979 Aug 23;280(5724):682–684. doi: 10.1038/280682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. L. Inquiries into the anatomical basis of olfactory discrimination. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):299–319. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham D., Woolsey T. A., Kruger L. Cellular localization of 2-[3H]deoxy-D-glucose from paraffin-embedded brains. J Neurosci. 1981 May;1(5):519–526. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-05-00519.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jourdan F., Duveau A., Astic L., Holley A. Spatial distribution of [14C]2-deoxyglucose uptake in the olfactory bulbs of rats stimulated with two different odours. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 21;188(1):139–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90563-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. S. Response patterns of amphibian olfactory bulb neurones to odour stimulation. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):695–715. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land L. J., Shepherd G. M. Autoradiographic analysis of olfactory receptor projections in the rabbit. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 26;70(3):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveteau J., MacLeod P. Olfactory discrimination in the rabbit olfactory glomerulus. Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):175–176. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Hubel D. H. Effects of sleep and arousal on the processing of visual information in the cat. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):554–561. doi: 10.1038/291554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton D. G. Spatial patterning of response to odors in the peripheral olfactory system. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jul;56(3):578–593. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.3.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sejnowski T. J., Reingold S. C., Kelley D. B., Gelperin A. Localization of[3H]-2-deoxyglucose in single molluscan neurones. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):449–451. doi: 10.1038/287449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp F. R., Kauer J. S., Shepherd G. M. Laminar analysis of 2-deoxyglucose uptake in olfactory bulb and olfactory cortex of rabbit and rat. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Jul;40(4):800–813. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. M. Synaptic organization of the mammalian olfactory bulb. Physiol Rev. 1972 Oct;52(4):864–917. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.4.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeen L. C. Odor-induced patterns of deoxyglucose consumption in the olfactory bulb of the tree shrew, Tupaia glis. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90871-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. B., Kauer J. S., Shepherd G. M. Functional organization of rat olfactory bulb analysed by the 2-deoxyglucose method. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jun 15;185(4):715–734. doi: 10.1002/cne.901850407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]