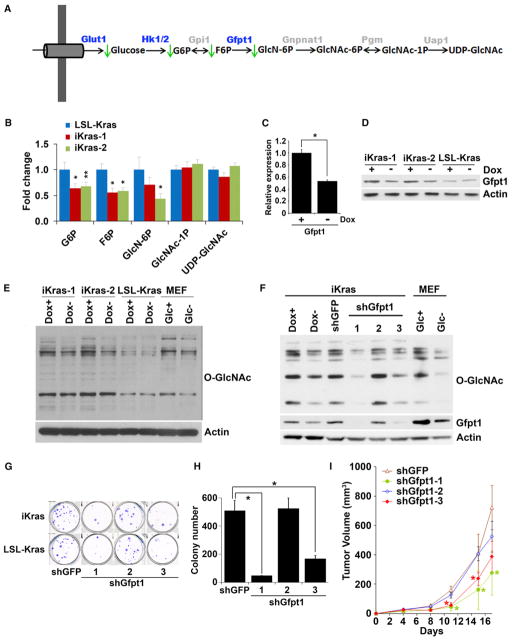
Figure 5. KrasG12D Inactivation Leads to Inhibition of the Hexosamine Biosynthesis Pathway and Protein O-Glycosylation.
(A) Summary of changes in the HBP upon KrasG12D inactivation. Metabolites that decrease upon doxy withdrawal are indicated with green arrows. Differentially expressed genes upon doxy withdrawal are highlighted in blue.
(B) Fold change of metabolites in the HBP upon doxy withdrawal for 24 hr.
(C and D) Relative mRNA (C) and protein levels (D) of Gfpt1 in the presence or absence of doxy for 24 hr.
(E) Western blot analysis for O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) levels in cells maintained in the presence or absence of doxy for 24 hr. For control samples, MEFs were cultured in the presence or absence of glucose for 24 hr.
(F) Western blot analysis for O-GlcNAc and Gfpt1 levels in cells infected with shRNA against GFP or Gfpt1.
(G and H) Clonogenic assay (G) and soft-agar colony formation assay (H) for iKras p53L/+ or LSL-Kras p53L/+ PDAC cells infected with shRNA against GFP or Gfpt1.
(I) iKras p53L/+ cell lines were infected with shRNA against GFP or Gfpt1 and subcutaneously injected into nude mice. Tumor volumes were measured and data shown are representative of results from three independent cell lines. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
Error bars represent SD of the mean. GlcNAc-1P, N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate; GlcNAc-6P, N-acetylglucosamine 6-phosphate; GlcN6P, glucosamine 6-phosphate; UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine. See also Figure S5.