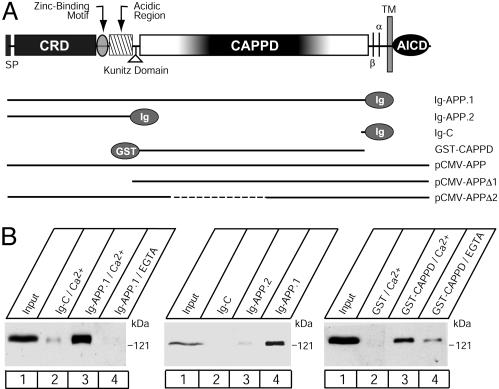
Fig. 1.
Binding of F-spondin to immobilized APP. (A) Domain structure of APP (Upper) and diagram of various APP vectors used for the present study (Lower). N-terminally, APP is composed of a signal peptide (SP), a CRD, a zinc-binding motif, acidic sequence regions, and a Kunitz domain. The center of APP is occupied by a large domain that contains no cysteine residues (referred to as CAPPD) and a short linker sequence that includes the cleavage sites for α- and β-secretases. C-terminally, APP contains a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail. The constructs used here include Ig-fusion proteins of the entire extracellular region or CRD alone (Ig-APP.1 or Ig-APP.2 respectively), a GST-CAPPD fusion protein, and expression vectors that encode full-length APP, or APP in which the CRD or part of the CAPPD were deleted marked by dashed lines (pCMV-APPΔ1 or 2, respectively). Nonneuronal APP contains an alternatively spliced Kunitz domain that is absent from all APP constructs used here. (B) Affinity chromatography of secreted myc-tagged recombinant F-spondin pull-downs on immobilized APP proteins. Ig- and GST-fusion proteins of various fragments of APP, as indicated in A, were used to affinity-purify secreted myc-tagged F-spondin produced in the supernatant of transfected COS cells.