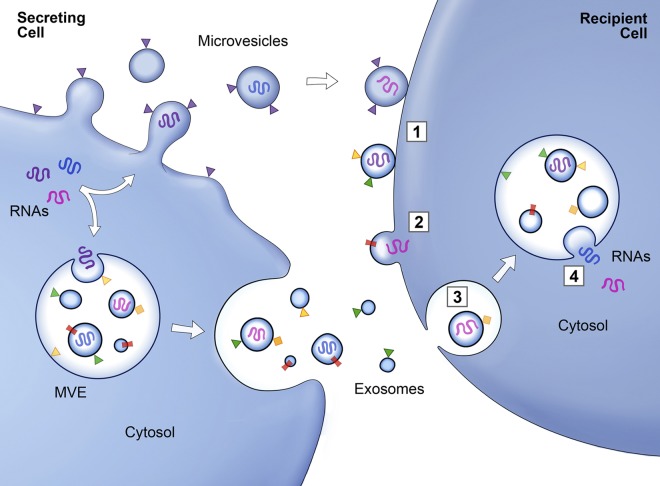
Figure 3.
Schematic of protein and RNA transfer by EVs. Membrane-associated (triangles) and transmembrane proteins (rectangles) and RNAs (curved symbols) are selectively incorporated into the ILV of MVEs or into MVs budding from the plasma membrane. MVEs fuse with the plasma membrane to release exosomes into the extracellular milieu. MVs and exosomes may dock at the plasma membrane of a target cell (1). Bound vesicles may either fuse directly with the plasma membrane (2) or be endocytosed (3). Endocytosed vesicles may then fuse with the delimiting membrane of an endocytic compartment (4). Both pathways result in the delivery of proteins and RNA into the membrane or cytosol of the target cell. Fusion and endocytosis are only represented for exosomal vesicles, but plasma membrane–derived MVs may have similar fates.