Abstract
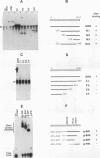
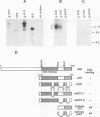
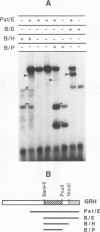
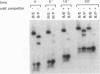
We have mapped the regions in the Drosophila melanogaster tissue-specific transcription factor Grainyhead that are required for DNA binding and dimerization. These functional domains correspond to regions conserved between Grainyhead and the vertebrate transcription factor CP2, which we show has similar activities. The identified DNA-binding domain is large (263 amino acids) but contains a smaller core that is able to interact with DNA at approximately 400-fold lower affinity. The major dimerization domain is located in a separate region of the protein and is required to stabilize the interactions with DNA. Our data also suggest that Grainyhead activity can be modulated by an N-terminal inhibitory domain.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel B., Sakonju S. Cell-type-specific mechanisms of transcriptional repression by the homeotic gene products UBX and ABD-A in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1099–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi L. D., Tjian R. Drosophila tissue-specific transcription factor NTF-1 contains a novel isoleucine-rich activation motif. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1341–1353. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray S. J., Burke B., Brown N. H., Hirsh J. Embryonic expression pattern of a family of Drosophila proteins that interact with a central nervous system regulatory element. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1130–1145. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray S. J., Kafatos F. C. Developmental function of Elf-1: an essential transcription factor during embryogenesis in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1672–1683. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Pirrotta V. Multimerization of the Drosophila zeste protein is required for efficient DNA binding. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2075–2083. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevray P. M., Nathans D. Protein interaction cloning in yeast: identification of mammalian proteins that react with the leucine zipper of Jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5789–5793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Attardi L. D., Admon A., Freeman M., Tjian R. Functional analysis of NTF-1, a developmentally regulated Drosophila transcription factor that binds neuronal cis elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1677–1688. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Spann D. R., Posakony J. W. extramacrochaetae, a negative regulator of sensory organ development in Drosophila, defines a new class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90212-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrell J., Modolell J. The Drosophila extramacrochaetae locus, an antagonist of proneural genes that, like these genes, encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegde R. S., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure at 1.7 A of the bovine papillomavirus-1 E2 DNA-binding domain bound to its DNA target. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):505–512. doi: 10.1038/359505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. G., Swendeman S. L., Barnhart K. M., Sheffery M. Promoter elements and erythroid cell nuclear factors that regulate alpha-globin gene transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5958–5966. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Herrmann B. G. The Brachyury gene encodes a novel DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3211–3220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Yu V. C., När A., Kyakumoto S., Han Z., Silverman S., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Differential orientations of the DNA-binding domain and carboxy-terminal dimerization interface regulate binding site selection by nuclear receptor heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1423–1435. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A. Dimeric transcription factor families: it takes two to tango but who decides on partners and the venue? J Cell Sci. 1992 Sep;103(Pt 1):9–14. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. C., Swendeman S. L., Sheffery M. Molecular cloning of the alpha-globin transcription factor CP2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):828–835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Haroun R. I., Clos J., Wisniewski J., Wu C. Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.8421783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rost B., Sander C. Jury returns on structure prediction. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):540–540. doi: 10.1038/360540b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A germline transformation analysis reveals flexibility in the organization of heat shock consensus elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2971–2988. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Characterization of a dimerization motif in AP-2 and its function in heterologous DNA-binding proteins. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1067–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.1998122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]