Abstract
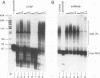
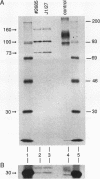
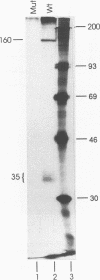
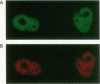
During the formation of the 3' ends of mRNA, the cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) is required for 3' cleavage of the transcript as well as for subsequent polyadenylation. Using peptide sequences from a tryptic digest, we have cloned the 100-kDa subunit of CPSF. This subunit is a novel protein showing no homology to any known polypeptide in databases. Polyclonal antibodies against the C terminus of the protein inhibit the polyadenylation reaction. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies were used to characterize the composition of CPSF. Immunoprecipitations of CPSF from HeLa cell extracts and from labeled chromatographic fractions show the coprecipitation of all four subunits of 160, 100, 73, and 30 kDa. Proteins of 160 and 30 kDa that are specifically cross-linked to precursor RNA by UV irradiation were identified as CPSF subunits by immunoprecipitation. Immunofluorescent detection of CPSF in HeLa cells localized it in the nucleoplasm, excluding cytoplasm and nucleolar structures.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell V. J., Wickens M., Bienroth S., Keller W., Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I. Site-directed ribose methylation identifies 2'-OH groups in polyadenylation substrates critical for AAUAAA recognition and poly(A) addition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90414-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienroth S., Keller W., Wahle E. Assembly of a processive messenger RNA polyadenylation complex. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):585–594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienroth S., Wahle E., Suter-Crazzolara C., Keller W. Purification of the cleavage and polyadenylation factor involved in the 3'-processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19768–19776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosi R., Hauri H. P., Krämer A. Separation of splicing factor SF3 into two components and purification of SF3a activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17640–17646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Tollervey D., Pepperkok R., Barabino S. M., Merdes A., Brunner C., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurt E., Lamond A. I. Mammalian nuclei contain foci which are highly enriched in components of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):195–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. Poly(A) polymerase purified from HeLa cell nuclear extract is required for both cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):193–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R. The cap and poly(A) tail function synergistically to regulate mRNA translational efficiency. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2108–2116. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson S. I., Beyer K., Martin G., Keller W., Boelens W. C., Mattaj L. W. The human U1A snRNP protein regulates polyadenylation via a direct interaction with poly(A) polymerase. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Bienroth S., Lang K. M., Christofori G. Cleavage and polyadenylation factor CPF specifically interacts with the pre-mRNA 3' processing signal AAUAAA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4241–4249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause S., Fakan S., Weis K., Wahle E. Immunodetection of poly(A) binding protein II in the cell nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Sep;214(1):75–82. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz C. S., Alwine J. C. Direct interaction of the U1 snRNP-A protein with the upstream efficiency element of the SV40 late polyadenylation signal. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 1;8(5):576–586. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.5.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Proudfoot N. J. RNA 3' ends: formation and function--meeting review. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):259–264. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Chen J., Whoriskey J. Two proteins crosslinked to RNA containing the adenovirus L3 poly(A) site require the AAUAAA sequence for binding. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. G., Manley J. L. Characterization of the multisubunit cleavage-polyadenylation specificity factor from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14804–14811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Wickens M. Two phases in the addition of a poly(A) tail. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1401–1412. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Manley J. L. A human polyadenylation factor is a G protein beta-subunit homologue. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23471–23474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Manley J. L., MacDonald C. C., Wilusz J., Shenk T. A multisubunit factor, CstF, is required for polyadenylation of mammalian pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2112–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Four factors are required for 3'-end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1711–1724. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Berman C. H., Dull T. J., Gray A., Lee J. M. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene using a single synthetic DNA probe. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):361–364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. A novel poly(A)-binding protein acts as a specificity factor in the second phase of messenger RNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90119-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Keller W. RNA-protein interactions in mRNA 3'-end formation. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Aug;18(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00986771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Keller W. The biochemistry of 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:419–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. Purification and characterization of a mammalian polyadenylate polymerase involved in the 3' end processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3131–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman K. M., Steitz J. A. Association with terminal exons in pre-mRNAs: a new role for the U1 snRNP? Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):647–659. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T., Takagaki Y., Manley J. L. A multicomponent complex is required for the AAUAAA-dependent cross-linking of a 64-kilodalton protein to polyadenylation substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1244–1248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]