Abstract
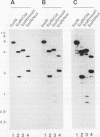
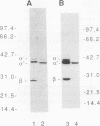
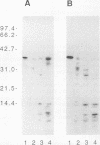
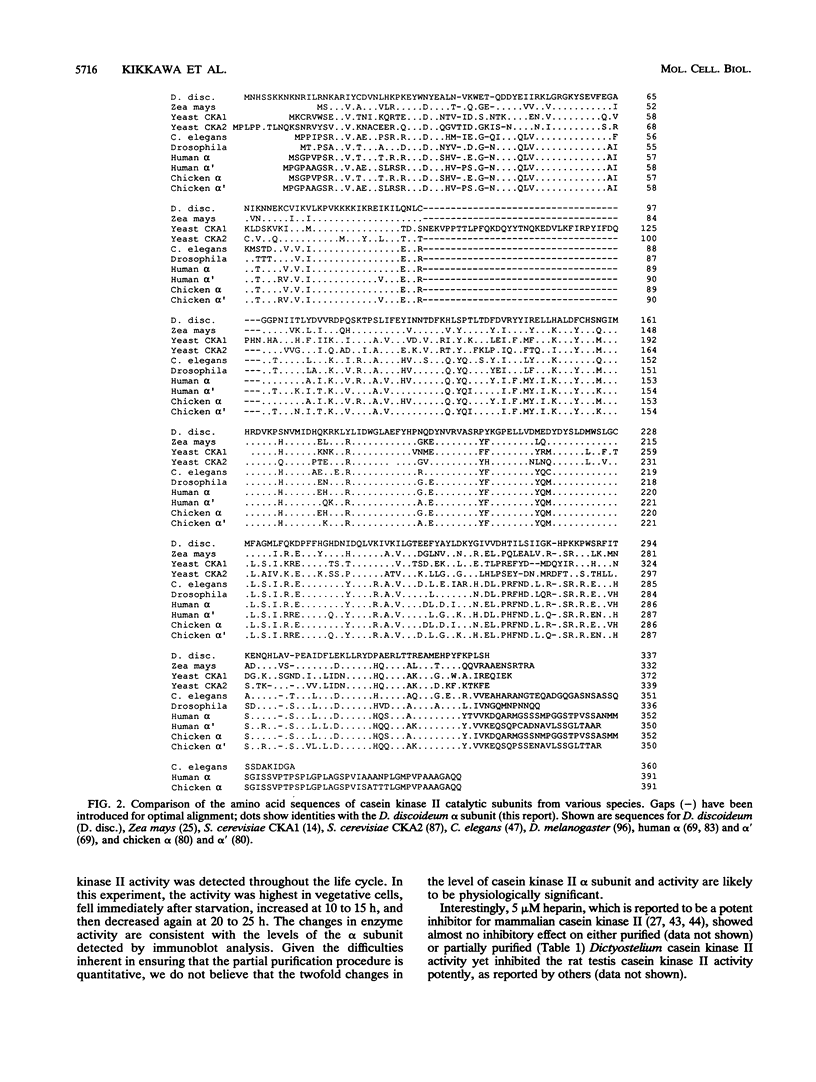
A Dictyostelium discoideum cDNA encoding an alpha-type subunit of casein kinase II was isolated, and its cDNA was used to study developmental expression of casein kinase II during the Dictyostelium life cycle. The 1.3-kb cDNA insert contained an open reading frame of 337 amino acids (M(r) 39,900). The deduced amino acid sequence has high homology with those of casein kinase II alpha subunits from other species. Genomic Southern blot analysis suggested that there is a single gene encoding casein kinase II alpha subunit in D. discoideum. Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that the casein kinase II alpha-subunit gene is expressed constitutively as a 1.9-kb mRNA throughout vegetative growth and multicellular development. Casein kinase purified from normal vegetative cells contained a major protein band of approximately 36 kDa, which was recognized by antisera raised against rat testis casein kinase II. Comparison of the in vitro transcription/translation product of the alpha-subunit cDNA clone and the purified 36-kDa protein by partial proteolysis indicated that the isolated cDNA clone encodes the Dictyostelium casein kinase II alpha subunit. No protein corresponding to a beta subunit was detected in purified casein kinase. Immunoblot analysis using anti-rat casein kinase II sera showed that the alpha subunit of casein kinase II is expressed constitutively like its mRNA during the life cycle of D. discoideum. Casein kinase II activity measured by using a specific peptide substrate paralleled the level of alpha subunit detected by immunoblotting during the life cycle, with a maximum variation of approximately 2-fold. We were unable to obtain disruptants of the casein kinase II alpha gene, suggesting that there is a single casein kinase II alpha gene, which is essential for vegetative growth of D. discoideum.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Stimulation of casein kinase II by epidermal growth factor: relationship between the physiological activity of the kinase and the phosphorylation state of its beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):821–825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman P., Osheroff N. Regulation of casein kinase II activity by epidermal growth factor in human A-431 carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11958–11965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agostinis P., Goris J., Pinna L. A., Merlevede W. Regulation of casein kinase 2 by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):785–789. doi: 10.1042/bj2480785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anjard C., Pinaud S., Kay R. R., Reymond C. D. Overexpression of Dd PK2 protein kinase causes rapid development and affects the intracellular cAMP pathway of Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):785–790. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Edmonds C., Fisher C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Vousden K. H. The region of the HPV E7 oncoprotein homologous to adenovirus E1a and Sv40 large T antigen contains separate domains for Rb binding and casein kinase II phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S. J., Cole M. D. Casein kinase II inhibits the DNA-binding activity of Max homodimers but not Myc/Max heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):166–176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldyreff B., Piontek K., Schmidt-Spaniol I., Issinger O. G. The beta subunit of casein kinase II: cloning of cDNAs from murine and porcine origin and expression of the porcine sequence as a fusion protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90140-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürki E., Anjard C., Scholder J. C., Reymond C. D. Isolation of two genes encoding putative protein kinases regulated during Dictyostelium discoideum development. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90538-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Dang Q., Glover C. V., Gasser S. M. Casein kinase II phosphorylates the eukaryote-specific C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Marshak D. R. Serum-stimulated cell growth causes oscillations in casein kinase II activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7345–7348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Santoro N., Marshak D. R. Regulating cell growth: casein-kinase-II-dependent phosphorylation of nuclear oncoproteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):91–95. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton L. A., Sanghera J. S., Clark-Lewis I., Pelech S. L. Structure-function analysis of casein kinase 2 with synthetic peptides and anti-peptide antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8840–8845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Wu J. L., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the CKA1 gene encoding the alpha subunit of yeast casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4981–4990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier M., de Gunzburg J., Veron M. Comparison of the regulatory and catalytic subunits of cAMP dependent protein kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum and bovine heart using polyclonal antibodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 29;136(2):651–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Oligomeric structure and catalytic activity of G type casein kinase. Isolation of the two subunits and renaturation experiments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Nellen W., Gomer R. H., Firtel R. A. Phenocopy of discoidin I-minus mutants by antisense transformation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côte G. P., Bukiejko U. Purification and characterization of a myosin heavy chain kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1065–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain gene by homologous recombination. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.3576222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. Dictyostelium discoideum: a model system for cell-cell interactions in development. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1054–1058. doi: 10.1126/science.2672337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolska G., Boldyreff B., Issinger O. G. Cloning and sequencing of the casein kinase 2 alpha subunit from Zea mays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 2;1129(1):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90230-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynes J. L., Firtel R. A. Molecular complementation of a genetic marker in Dictyostelium using a genomic DNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7966–7970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filhol O., Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Cytoplasmic and nuclear distribution of casein kinase II: characterization of the enzyme uptake by bovine adrenocortical nuclear preparation. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9928–9936. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filhol O., Cochet C., Delagoutte T., Chambaz E. M. Polyamine binding activity of casein kinase II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):945–952. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filhol O., Cochet C., Wedegaertner P., Gill G. N., Chambaz E. M. Coexpression of both alpha and beta subunits is required for assembly of regulated casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11133–11140. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Lodish H. F. A small nuclear precursor of messenger RNA in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):295–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., van Haastert P. J., Kimmel A. R., Devreotes P. N. G protein linked signal transduction pathways in development: dictyostelium as an experimental system. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90837-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Galloway D. A., Eisenman R. N., Lüscher B. The E7 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 is phosphorylated by casein kinase II. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Basset M., Blanchard J. M., Cavadore J. C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Casein kinase II induces c-fos expression via the serum response element pathway and p67SRF phosphorylation in living fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2921–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G. Cyclic AMP and other signals controlling cell development and differentiation in Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:853–879. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Antibody probing of western blots which have been stained with india ink. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomer R. H., Datta S., Mehdy M., Crowley T., Sivertsen A., Nellen W., Reymond C., Mann S., Firtel R. A. Regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:801–812. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grankowski N., Boldyreff B., Issinger O. G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant human casein kinase II subunits alpha and beta from bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Scheidtmann K. H., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A., Walter G. In vitro phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunzburg J., Veron M. A cAMP-dependent protein kinase is present in differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1063–1068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase II. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:317–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller-Harrison R. A., Meisner H., Czech M. P. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the beta subunit of human casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9053–9058. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt M., Nellen W. Differential antisense transcription from the Dictyostelium EB4 gene locus: implications on antisense-mediated regulation of mRNA stability. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu E., Rubin C. S. Casein kinase II from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cloning, characterization, and developmental regulation of the gene encoding the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19796–19802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu E., Rubin C. S. Casein kinase II from Caenorhabditis elegans. Properties and developmental regulation of the enzyme; cloning and sequence analyses of cDNA and the gene for the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5072–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu E., Rubin C. S. Expression of wild-type and mutated forms of the catalytic (alpha) subunit of Caenorhabditis elegans casein kinase II in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20609–20615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobi R., Voss H., Pyerin W. Human phosvitin/casein kinase type II. Molecular cloning and sequencing of full-length cDNA encoding subunit beta. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 15;183(1):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens P. M., Van Haastert P. J. Molecular basis of transmembrane signal transduction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):396–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.396-418.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez B., Pestaña A., Fernandez-Renart M. A phospholipid-stimulated protein kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):557–561. doi: 10.1042/bj2600557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessin R. H. Genetics of early Dictyostelium discoideum development. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):29–49. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.29-49.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization in Dictyostelium: unique structure at the 5'-ends of protein coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):541–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K., Czech M. P. Insulin-like growth factor I and insulin rapidly increase casein kinase II activity in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15872–15875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopatz I., Naiman T., Eli D., Canaani D. The nucleotide sequence of the mouse cDNA encoding the beta subunit of casein kinase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3639–3639. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N., Kuenzel E. A., Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Lüscher B., Sommercorn J. Casein kinase II as a potentially important enzyme concerned with signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Maridor G., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II is a predominantly nuclear enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):43–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Hadwiger J. A., Pupillo M., Firtel R. A. Molecular genetic analysis of two G alpha protein subunits in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1220–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichtling B. H., Majerfeld I. H., Spitz E., Schaller K. L., Woffendin C., Kakinuma S., Rickenberg H. V. A cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Dictyostelium discoideum. II. Developmental regulation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):662–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Frost J., Deng T., Smeal T., al-Alawi N., Kikkawa U., Hunter T., Brenner D., Karin M. Casein kinase II is a negative regulator of c-Jun DNA binding and AP-1 activity. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Cicirelli M. F., Harrylock M., Ericsson L. H., Piening C. J., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of the beta subunit of casein kinase II in human A431 cells. Identification of the autophosphorylation site and a site phosphorylated by p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20380–20389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Piening C., Sommercorn J., Takio K., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Subunit structure of casein kinase II from bovine testis. Demonstration that the alpha and alpha' subunits are distinct polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7638–7644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J. Detailed structure of the Drosophila melanogaster stellate genes and their transcripts. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):303–316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozeman F. J., Litchfield D. W., Piening C., Takio K., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding the alpha and the alpha' subunits of casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8436–8447. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Kuenzel E. A., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myc oncoproteins are phosphorylated by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1111–1119. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerfeld I. H., Leichtling B. H., Meligeni J. A., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. A cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Dictyostelium discoideum. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):654–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak J. R., de Bisschop N., Kris R. M., Prywes R. Casein kinase II enhances the DNA binding activity of serum response factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):955–967. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Firtel R. A. A developmentally regulated, putative serine/threonine protein kinase is essential for development in Dictyostelium. Mech Dev. 1991 Sep;35(2):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90060-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Firtel R. A. Cyclic AMP regulation of early gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum: mediation via the cell surface cyclic AMP receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):458–469. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Firtel R. A. Two-phase regulatory pathway controls cAMP receptor-mediated expression of early genes in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R. M., Hsuan J. J., McGuigan C., Wynne J., Treisman R. Casein kinase II phosphorylation increases the rate of serum response factor-binding site exchange. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):97–105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maridor G., Park W., Krek W., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II. cDNA sequences, developmental expression, and tissue distribution of mRNAs for alpha, alpha', and beta subunits of the chicken enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2362–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Simon S., Kikkawa U., Eckhart W. The p53 tumour suppressor protein is phosphorylated at serine 389 by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3253–3260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Czech M. P. Phosphorylation of transcriptional factors and cell-cycle-dependent proteins by casein kinase II. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90076-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Heller-Harrison R., Buxton J., Czech M. P. Molecular cloning of the human casein kinase II alpha subunit. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):4072–4076. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutzel R., Lacombe M. L., Simon M. N., de Gunzburg J., Veron M. Cloning and cDNA sequence of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Datta S., Reymond C., Sivertsen A., Mann S., Crowley T., Firtel R. A. Molecular biology in Dictyostelium: tools and applications. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:67–100. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61637-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ospina B., Fernández-Renart M. Characterization of three casein kinases type I from Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):483–488. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90159-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabha R., Chen-Wu J. L., Hanna D. E., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the yeast CKA2 gene: casein kinase II is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen E., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of casein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5586–5590. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez M., Grande J., Itarte E. Developmental changes in rat hepatic casein kinases 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):493–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent C., Lasko D. D., Kodama K., Woodgett J. R., Lindahl T. Activation of mammalian DNA ligase I through phosphorylation by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2925–2933. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pupillo M., Klein P., Vaughan R., Pitt G., Lilly P., Sun T., Devreotes P., Kumagai A., Firtel R. cAMP receptor and G-protein interactions control development in Dictyostelium. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):657–665. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Spudich J. A. Myosin heavy chain kinase from developed Dictyostelium cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15144–15150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart M. F., Sastre L., Sebastián J. Purification and properties of cAMP-independent nuclear protein kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):47–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino S., Mann S. K., Hori R. T., Pinko C., Firtel R. A. Molecular analysis of a developmentally regulated gene required for Dictyostelium aggregation. Dev Biol. 1989 Jan;131(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding alpha and beta subunits of Drosophila melanogaster casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3409–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. R., Reichert G. H., Issinger O. G. Enhanced casein kinase II activity during mouse embryogenesis. Identification of a 110-kDa phosphoprotein as the major phosphorylation product in mouse embryos and Krebs II mouse ascites tumor cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):733–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh T. J., Huang K. P. Glycogen synthase (casein) kinase-1: tissue distribution and subcellular localization. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Mulligan J. A., Lozeman F. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of casein kinase II in response to insulin and to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Introductory remarks and some biochemical considerations. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:3–8. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61634-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. J., Van Haastert P. J., Devreotes P. N. Surface cAMP receptors mediate multiple responses during development in Dictyostelium: evidenced by antisense mutagenesis. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Kuenzel E. A., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Amino acid sequence of the beta subunit of bovine lung casein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. L., Spudich J. A. Dictyostelium myosin light chain kinase. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13818–13824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitz T., Eli D., Penner M., Bakhanashvili M., Naiman T., Timme T. L., Wood C. M., Moses R. E., Canaani D. Expression of the cDNA for the beta subunit of human casein kinase II confers partial UV resistance on xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;236(1):85–97. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Lin W. J., Takada-Axelrod F., Tuazon P. T. Importance of subunit interactions in regulation of casein kinase II. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:224–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Transmembrane signal transduction pathways in Dictyostelium. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:185–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu I. J., Spector D. L., Bae Y. S., Marshak D. R. Immunocytochemical localization of casein kinase II during interphase and mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1217–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Franke J., Kessin R. H., Véron M. Detection and developmental regulation of the mRNA for the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of D. discoideum by cell-free translation. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):363–367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]