Fig 4.
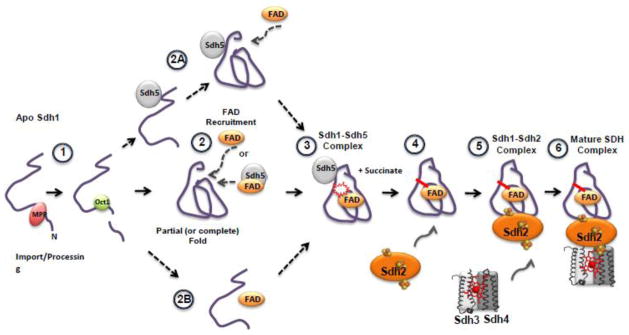
A general conceptual model of Sdh1 flavinylation and subsequent assembly into the SDH complex. (1) After import of Sdh1 into the matrix, processing of the presequence (predicted to be by proteases MPP and Oct1 [62]) occurs. Flavinylation has been shown to occur only to the processed peptide [61,63]. (2) Apo-Sdh1 presumably folds into a structure resembling that of holo-Sdh1 [32,61,64]. After the organized structure has formed, the FAD binding pocket could accept the cofactor and succinate, stabilizing Sdh1 from degradation. FAD recruitment may occur via Sdh5-mediated delivery or as “free” FAD. Alternative pathways after processing include (2A) Sdh5 mediated folding of Sdh1, (2B) FAD binding to a nascent structure of Sdh1 followed by folding into a holo-structure. (3) Formation of the Sdh1-Sdh5 complex and subsequent covalent bond formation. This complex can be purified or visualized using native gel electrophoresis. TCA cycle intermediates like succinate greatly enhances the covalent bond formation [53]. (4) Association with Sdh2. Currently, a trimeric complex consisting of Sdh1-Sdh2-Sdh5 has not been identified. (5) Association with the Sdh3 and Sdh4 membrane subunits and the (6) formation of the mature SDH complex anchored in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
