Table 1.
Selected inhibitors of FGF signalling
| Drug | structure | Function | refs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunitinib |

|
|
62 |
| Suramin |

|
|
103–107 |
| Thalidomide |
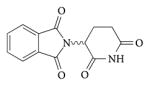
|
|
100–102 |
| SU5402 |

|
63–65 | |
| PD173074 |

|
||
| NDGA |

|
FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; NDGA, norhydroguaiaretic acid; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.
