Figure 2.
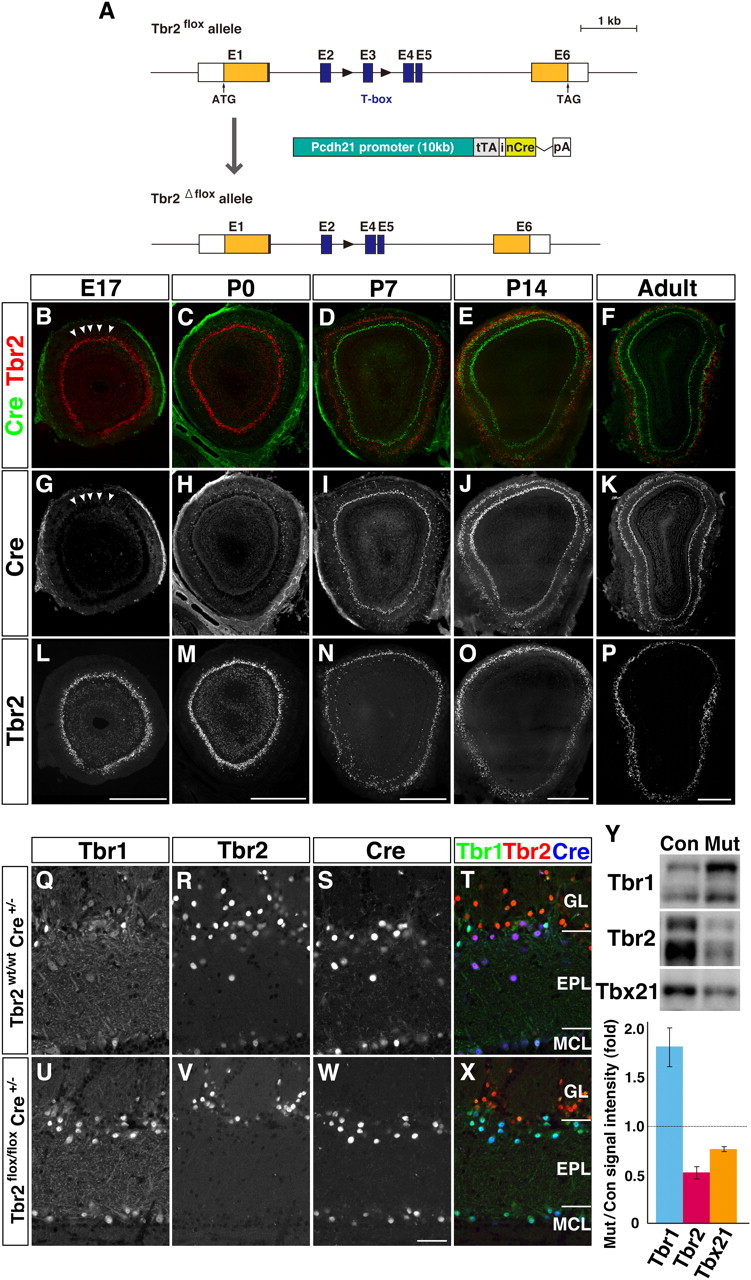
Tbr1 upregulation in Tbr2-deficient mitral and tufted cells. A, Generation of mitral/tufted cell-specific Tbr2 conditional knockout mice. Genomic organization of Tbr2flox allele, Tbr2flox allele, and Pcdh21-Cre transgene construct. Black triangles represent loxP sites. Pcdh21-Cre transgene includes tTA (tetracycline transactivator) and nCre (Cre recombinase with a nuclear localization signal) intervened by internal ribosome entry sequence (i) from human fibroblast growth factor 2 gene, followed by a rabbit β-globin polyadenylation signal (pA). B–P, Expression of Cre recombinase (green) and Tbr2 (red) in OB coronal sections of developing and adult Tbr2 conditional knockout (Tbr2flox/flox Cre+/−) mice. Cre protein is first detectable in mitral cells in the dorsal region of the OB at E17 (B, G; arrowheads). At P14 and later, Cre is strongly expressed in all the mitral and tufted cells where Tbr2 protein is specifically lost. Q–X, Triple immunofluorescence labeling of Tbr1 (Q, U), Tbr2 (R, V), and Cre (S, W) on adult OB coronal sections from Tbr2wt/wt; Cre+/− (Q–T) and Tbr2flox/flox; Cre+/− (U–X) mice. T, X, merged images (Tbr1, green; Tbr2, red; Cre, blue). Tbr2 protein is detectable in Cre-expressing mitral and tufted cells of Tbr2wt/wt mice (R–T), but not of Tbr2flox/flox mice (V–X). On the contrary, Tbr1 expression is increased in Cre-positive mitral and tufted cells in Tbr2flox/flox mice (U, W, X). Y, Quantification of Tbr1 subfamily proteins. OB homogenates from control (Con) and Tbr2 conditional knockout mice (Mut) were subjected to Western blot analysis. Intensity of each band was measured and statistically analyzed (bottom; values are mean ± SEM, n = 3 for each). For Tbr1 and Tbr2, intensities of both upper and lower bands were added. In Tbr2 conditional knockout mice, the amount of Tbr1 protein is increased by 1.82 ± 0.16-fold compared with control littermates, while Tbx21 protein is decreased by 0.76 ± 0.01-fold. Scale bars: B–P, 500 μm; Q–X, 50 μm.
