Table 1. Top predicted ASD risk genes from the TADA analysis of combined ASD data (de novo, inherited and case-control).
| Loss of function (LoF) | |||||||
| Gene | De novo | Transmitted | Nontransmitted | Case | Control | p dn | p TADA(LoF) |
| KATNAL2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3.1×10−6 | 2×10−7 |
| CHD8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 9.5×10−5 | 2.4×10−6 |
| LMCD1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.067 |
| S100G | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0.00042 | 1.6×10−5 |
| DYRK1A | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.6×10−6 | 4.3×10−6 |
| PPM1D | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0.0032 | 0.00023 |
| SCN2A | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.9×10−5 | 2.8×10−5 |
| CUL3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0.004 | 0.00013 |
| DEAF1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.031 |
| BANK1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0.0064 |
| POGZ | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3×10−5 | 1.4×10−5 |
| WDR55 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.18 |
| FAM91A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0046 | 0.0019 |
| COL25A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0.0034 | 2.3×10−5 |
The  column shows the p-values using the De Novo Test from the de novo LoF mutations alone. The
column shows the p-values using the De Novo Test from the de novo LoF mutations alone. The  column shows the p-values from the TADA test using all LoF data. The
column shows the p-values from the TADA test using all LoF data. The 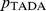 column shows the p-values from the TADA test using both LoF and Mis3 data. The star symbols mark the double-hit genes that were reported in earlier publications. C1orf95 also has q-value<.2, however this signal is based entirely on 11 identical Mis3 variants in cases and 0 in controls. This allele is common in African populations [40]. While the AASC sample is of European ancestry, a portion of it, largely from Portugal, carries some sub-Saharan alleles [7]. Thus, this signal is likely due to population substructure. Similarly, the 3 LoF variants seen in S100G are copies of a splice variant that is common in African populations, so this result should be viewed with caution.
column shows the p-values from the TADA test using both LoF and Mis3 data. The star symbols mark the double-hit genes that were reported in earlier publications. C1orf95 also has q-value<.2, however this signal is based entirely on 11 identical Mis3 variants in cases and 0 in controls. This allele is common in African populations [40]. While the AASC sample is of European ancestry, a portion of it, largely from Portugal, carries some sub-Saharan alleles [7]. Thus, this signal is likely due to population substructure. Similarly, the 3 LoF variants seen in S100G are copies of a splice variant that is common in African populations, so this result should be viewed with caution.
